5G Infrastructure Market Size, Demand & Outlook | 40.2% CAGR
Global 5G Infrastructure Market Size, Share & Analysis By Component (Hardware, Services), By Spectrum (Sub-6 GHz, mmWave), By Network Architecture (Standalone, Non-standalone), By Vertical Industry (Manufacturing, Automotive and Transportation, Enterprise/Corporate, Energy & Utilities, Healthcare/Hospitals, Smart Cities, Others) Industry Dynamics, Rollout Strategies & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
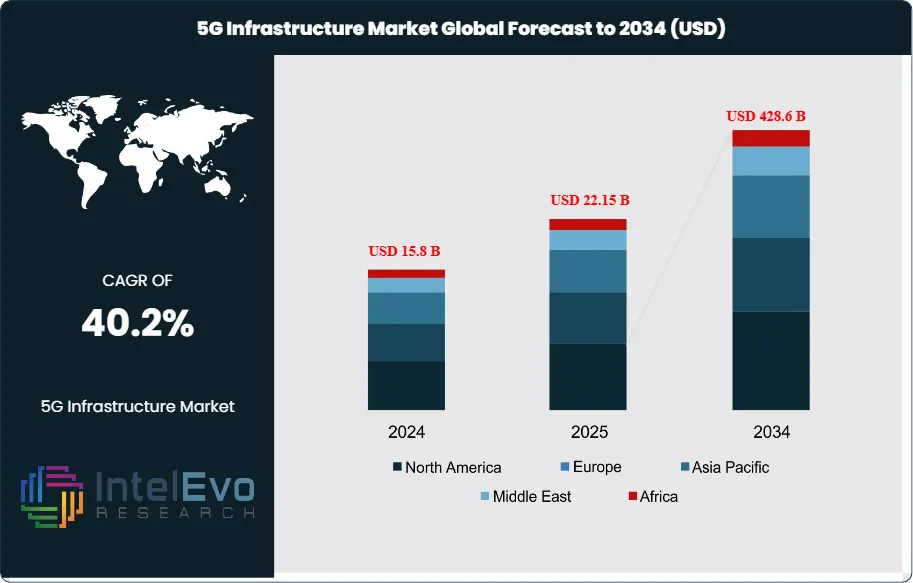
The 5G Infrastructure Market was valued at approximately USD 15.8 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach nearly USD 428.6 Billion by 2034, growing at an estimated CAGR of around 40.2% from 2025 to 2034. The rapid surge in smart devices, autonomous mobility, and industrial automation is accelerating global 5G deployment. Massive MIMO, small cells, and edge computing are becoming core components of next-gen connectivity. With telecom operators and governments boosting large-scale network investments, 5G is entering a hyper-growth decade, reshaping digital economies worldwide.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportHaving moved beyond experimental deployments observed between 2019 and 2021, the sector has entered a new phase marked by broader implementation. Current investment patterns suggest a growing shift toward modern core network architectures, extensive fiber deployment, and the installation of compact, high-density cell sites.
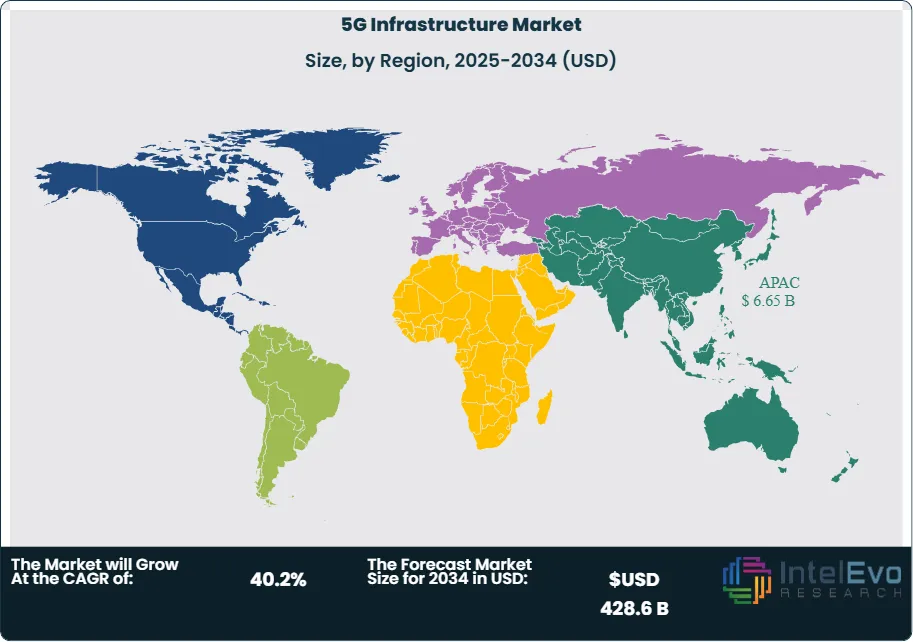
Asia Pacific stood out in 2024 as the highest-earning region, contributing over 42% of the total market revenue. This dominance reflects robust government-led 5G initiatives and heavy infrastructure investment by telecom operators. Meanwhile, the North American and European markets are progressing steadily, focusing on mid-band frequency rollouts and advancing toward full standalone 5G network capabilities.
The explosive rise in mobile data usage has been a key force behind this growth. Monthly global data traffic reached around 130 exabytes in 2024 and is projected to triple by the end of the decade. Alongside this, the increasing presence of interconnected devices and industrial IoT systems is creating the need for networks that can guarantee minimal latency and exceptional reliability.
Commercial and enterprise applications are playing a pivotal role in shaping demand. The rollout of fixed wireless internet services for homes and businesses, alongside the rise of private 5G networks in manufacturing and logistics, is expanding the market’s reach. Additionally, industries like healthcare, automotive, and digital media are adopting 5G to support advanced, real-time operations. On the supply side, technological innovation is helping reduce deployment costs. Hardware improvements, like new radio technologies and enhanced chipsets, as well as the rise of virtual network solutions, are making 5G deployment more cost-effective and scalable.
Policymakers are also facilitating growth by accelerating spectrum licensing and simplifying approval processes for infrastructure installation. However, several challenges remain. Telecom providers must be cautious with capital expenditures, given the long return cycles. In urban areas, gaining approvals for installing compact cell stations is often slow and fragmented. On top of that, operators are dealing with rising operational costs, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and a complex global supply chain that’s sensitive to political dynamics.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the way networks are built and operated. In congested city environments, smart antenna systems are increasing throughput, while the transition to standalone network cores is enabling advanced features like real-time network customization and low-latency communication for critical tasks. Edge computing is also gaining momentum, shifting processing tasks closer to end users to enhance performance. Meanwhile, open network standards and software-defined approaches are improving compatibility and speeding up deployment cycles, while fiber-based backhaul systems are enhancing end-to-end connectivity.
Regionally, Asia Pacific is expected to remain at the forefront of 5G expansion, due to government-backed digital initiatives and sector-wide modernization. North America is projected to accelerate its adoption of private and fixed wireless networks, especially in underserved areas. Europe is advancing gradually, with a strong emphasis on uniform regulatory practices and manufacturing use cases. The Middle East, on the other hand, is gaining global attention through its investment in digital infrastructure as part of new smart city developments.
Looking ahead, investment opportunities are likely to center on urban densification of network infrastructure, deployment of cloud-native core software, and establishment of localized edge data centers. Solutions focused on logistics, utilities, and automated manufacturing—especially those using private 5G networks—are also expected to be among the most attractive segments for investors and technology vendors alike.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The global 5G Infrastructure market will expand from USD 15.8 Billion in 2024 to USD 428.6 Billion by 2034 at a 40.2% CAGR (2025–2034), propelled by densification of radio access networks (RAN), fiberized backhaul, and migration to cloud-native cores.
- Component: Hardware led in 2024 with 80.5% revenue share, reflecting intensive rollouts of antennas, small cells, and massive MIMO RAN; near term, spend remains capex-heavy while software/core and automation layers scale post-NSA stabilization.
- Frequency Band: Sub-6 GHz accounted for 86.3% of deployments in 2024, favored for its coverage–capacity balance in urban/suburban grids; mmWave remains targeted to high-density venues and fixed wireless access where ultra-capacity justifies cost.
- Deployment Architecture: Non-Standalone (NSA) captured 61% share in 2024 as operators leveraged 4G cores for speed-to-market; Standalone (SA) is set to accelerate with network slicing and URLLC use cases unlocking new service revenues.
- Driver: Exploding data demand is stretching legacy networks—global monthly mobile data traffic reached ~130 EB in 2024 and is projected to triple to ~403 EB by 2029—pressing operators and enterprises to invest in high-capacity 5G RAN and core upgrades.
- Restraint: Monetization lag and cost intensity weigh on returns—an 80.5% hardware mix and 61% NSA dependence skew spend to infrastructure while delaying SA-driven premium services, constraining near-term free cash flow and lengthening payback cycles.
- Opportunity: Industrial private 5G—anchored by manufacturing (the top vertical at 23.8% share in 2024)—offers high-growth potential via robotics, machine vision, and digital twins; adjacent hotspots include logistics hubs, energy sites, and hospital campuses.
- Trend: Open RAN, virtualized RAN, and AI/ML-driven automation are shifting value to software, improving spectral efficiency and operating economics; early SA rollouts are piloting network slicing SLAs for media uplink, mission-critical IoT, and edge analytics.
- Regional Analysis: APAC led with 42.1% share (USD 5.7 billion) in 2024 on aggressive national programs and enterprise digitization; North America is scaling SA cores and FWA, Europe advances manufacturing-centric private 5G, and the Middle East/India emerge as investment hotspots via greenfield smart-city and industrial corridors.
Component Analysis
Hardware remains the economic backbone of 5G buildouts. In 2024, physical infrastructure (RAN, core, transport, small cells) captured ~80.5% of market revenue, reflecting intensive densification, fiberized backhaul/fronthaul, and massive-MIMO upgrades. Through 2025–2028, operators in APAC, North America, and parts of Europe are prioritizing mid-band overlays and small-cell grids to relieve traffic hot spots, sustaining a hardware-heavy mix even as unit costs fall.
That said, Services are set to outgrow the base, propelled by Standalone (SA) migrations, private 5G design–build–operate models, and lifecycle automation. Managed services, RAN optimization, and security will expand faster than total market CAGR as enterprises seek guaranteed SLAs for latency and reliability, while operators outsource operations to compress opex and accelerate time-to-value.
Spectrum Analysis
Sub-6 GHz is the workhorse of nationwide 5G. It accounted for ~86.3% of deployments in 2024 and will remain the coverage foundation through the decade due to favorable propagation, indoor penetration, and compatibility with refarmed LTE spectrum. Continuous improvements in beamforming and multi-band radios are lifting spectral efficiency, enabling operators to meet rising data loads without linear capex growth.
mmWave will scale more selectively where ultra-capacity economics pencil out—dense venues, fixed wireless access (FWA), industrial campuses, and transport hubs. As device ecosystems mature and integrated access/backhaul (IAB) reduces fiber dependence, mmWave contribution to new adds increases post-2026, particularly in North America, Japan, and the Gulf, though overall share remains secondary to Sub-6 for wide-area mobility.
Network Architecture Analysis
Non-standalone (NSA) dominated in 2024 (~61% share) by leveraging existing 4G cores for speed-to-market and capex efficiency. NSA will continue supporting enhanced mobile broadband and FWA where rapid capacity is paramount, especially in suburban footprints and emerging markets scaling first-phase 5G.
From 2025 onward, Standalone (SA) becomes the strategic pivot. SA cores unlock network slicing, ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), exposure APIs, and deterministic QoS required by mission-critical IoT. As slicing pilots move to commercial SLAs and enterprise edge nodes proliferate, SA’s share rises each year, despite transitional challenges (device readiness, integration complexity, and security hardening).
Vertical Analysis
Manufacturing leads enterprise demand (≈23.8% share in 2024) as factories deploy private 5G for robotics, machine vision, AGVs, and digital twins. Low jitter and high uplink performance reduce defects and downtime, while predictive maintenance and real-time quality analytics compress cycle times—key in autos, electronics, and process industries.
Automotive & Transportation, Energy & Utilities, and Healthcare are fast followers. Smart ports, rail yards, and airports are adopting 5G for asset tracking and safety systems; utilities are piloting field-area networks and substation automation; hospitals employ 5G for high-resolution imaging transfer and connected care. Smart-city programs—video analytics, V2X corridors, and public safety—create multi-tenant demand that benefits both public and private networks.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific remains the largest and most dynamic region (≈42.1% share; USD ~5.7 billion in 2024), underpinned by aggressive national programs and deep local supply chains. China’s expansive base-station footprint (well over three million sites by 2024) and India’s rapid mid-band rollout are catalysts for regional scale, while Japan and South Korea continue to push SA, edge, and enterprise private 5G use cases.
North America is a profitability-focused market, emphasizing SA core upgrades, mmWave/FWA capacity layers, and private-network partnerships for industrial campuses. Europe is accelerating spectrum harmonization and industry-centric private 5G—particularly in Germany, the Nordics, and the UK—balancing coverage goals with manufacturing digitalization. Latin America advances through staggered auctions and FWA economics in underserved areas, and the Middle East & Africa are emerging investment hotbeds, leveraging greenfield smart-city initiatives and industrial corridors to jump-start high-capacity 5G deployments post-2025.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMarket Key Segments
By Component
- Hardware
- Radio Access Network (RAN)
- Core Network
- Others
- Services
By Spectrum
- Sub-6 GHz
- mmWave
By Network Architecture
- Standalone
- Non-standalone
By Vertical Industry
- Manufacturing
- Automotive and Transportation
- Enterprise/Corporate
- Energy & Utilities
- Healthcare/Hospitals
- Smart Cities
- Others
Regions
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 15.8 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 428.6 B |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 40.2% |
| Historical data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | By Component (Hardware, Services), By Spectrum (Sub-6 GHz, mmWave), By Network Architecture (Standalone, Non-standalone), By Vertical Industry (Manufacturing, Automotive and Transportation, Enterprise/Corporate, Energy & Utilities, Healthcare/Hospitals, Smart Cities, Others) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | CommScope Holding Company Inc., NEC Corporation, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd, ZTE Corporation, Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, Qualcomm Technologies Inc., Cisco Systems Inc., Airspan Networks Inc., Nokia Corporation, Oracle Corporation, Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP, Mavenir Systems Inc., Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd, Qucell Networks Co. Ltd, Other Key Players |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the 5G Infrastructure Market?
The global 5G Infrastructure Market will rise from USD 15.8B in 2024 to USD 428.6B by 2034, driven by massive MIMO, small cells, and rapid industrial automation adoption.
Who are the major players in the 5G Infrastructure Market?
CommScope Holding Company Inc., NEC Corporation, Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd, ZTE Corporation, Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, Qualcomm Technologies Inc., Cisco Systems Inc., Airspan Networks Inc., Nokia Corporation, Oracle Corporation, Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP, Mavenir Systems Inc., Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd, Qucell Networks Co. Ltd, Other Key Players
Which segments covered the 5G Infrastructure Market?
By Component (Hardware, Services), By Spectrum (Sub-6 GHz, mmWave), By Network Architecture (Standalone, Non-standalone), By Vertical Industry (Manufacturing, Automotive and Transportation, Enterprise/Corporate, Energy & Utilities, Healthcare/Hospitals, Smart Cities, Others)
How can this market research report help my business make strategic decisions?
Our market research reports provide actionable intelligence, including verified market size data, CAGR projections, competitive benchmarking, and segment-level opportunity analysis. These insights support strategic planning, investment decisions, product development, and market entry strategies for enterprises and startups alike.
How frequently is the data updated?
We continuously monitor industry developments and update our reports to reflect regulatory changes, technological advancements, and macroeconomic shifts. Updated editions ensure you receive the latest market intelligence.
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date