Aircraft Maintenance Market 2024–2034 | Size & 6.3% CAGR
Global Aircraft Maintenance Market Size, Share & Analysis By Maintenance Type (Engine, Line Maintenance, Airframe, Components, Others), By Aircraft Type (Narrow-body Aircrafts, Wide-body Aircrafts, Others), By End-Use (Commercial, Military, Others) Industry Regions & Key Players – Fleet Aging Trends, Digital MRO Adoption & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
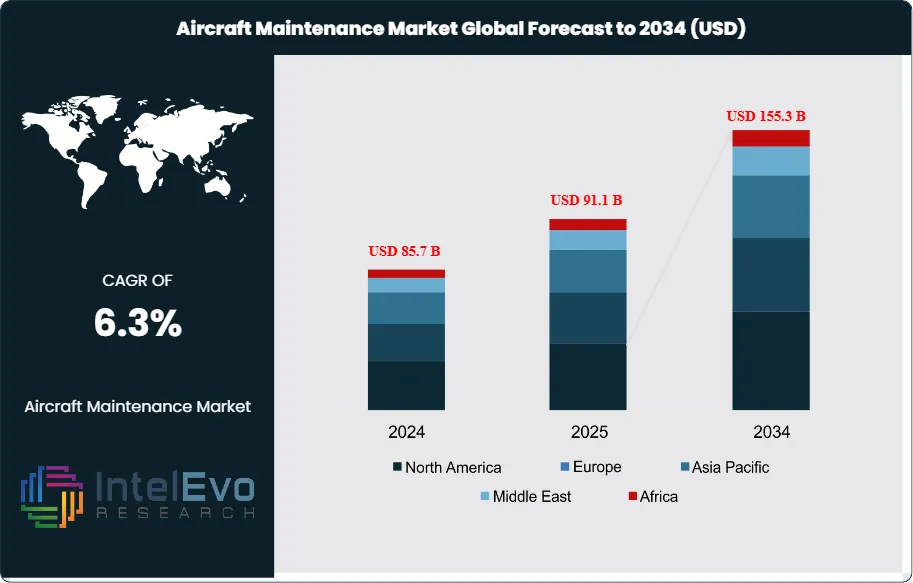
The Aircraft Maintenance Market is valued at USD 85.7 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach around USD 155.3 billion by 2034, registering a steady CAGR of approximately 6.3% during 2025–2034. This growth reflects rising global flight hours, accelerated fleet expansion across commercial and regional aviation, and increased reliance on predictive maintenance technologies. Airlines are rapidly upgrading MRO capabilities with AI-driven diagnostics and digital twins to reduce AOG time and improve turnaround efficiency. As sustainability regulations tighten, demand for engine retrofits, lightweight components, and next-gen maintenance solutions is gaining strong traction across industry platforms.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMomentum reflects the steady expansion of the active fleet, rising utilization, and the maturing post-pandemic replacement cycle. Historically, spend has tracked available seat kilometers and fleet age; as narrow-body aircraft dominate new deliveries, line maintenance and quick-turn checks are growing faster, while heavy airframe overhauls normalize from earlier deferrals. Engine and component work continue to anchor value pools—industry benchmarks often place engine MRO near ~40–45% of total spend—supported by extended on-wing times and shop-visit intensity as next-generation turbofans age into mid-life.
Demand is propelled by the proliferation of low-cost carriers, heightened passenger-safety expectations, and the complexity of modern airframes and engines, which require specialized tooling and skills. Regulatory rigor remains a central force: roughly 80% of maintenance tasks are performed to meet mandates from authorities such as the FAA and EASA, and the FAA requires at least 16 hours of annual training per technician, sustaining a vibrant ecosystem for continuous education and certification. Talent is a critical bottleneck: Boeing estimates the industry will need ~600,000 maintenance technicians worldwide, sharpening competition for skilled labor and incentivizing automation, remote expertise, and collaborative robotics to lift productivity. Cost pressures, supply-chain variability for advanced materials and parts, and hangar capacity constraints remain key challenges, particularly at peak seasonal demand.
Technology is reshaping the maintenance paradigm. Predictive and condition-based maintenance (CBM), enabled by aircraft health monitoring, digital twins, and AI-driven analytics, is reducing unscheduled events and turnaround times; RFID/IoT tracking is streamlining parts traceability and compliance. Cloud-based maintenance information systems and mobile e-logbooks are accelerating task execution and documentation accuracy, while additive manufacturing for non-critical components and smart borescopes are shortening shop cycles.
Regionally, North America and Europe retain the largest installed bases and deep MRO networks, while Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing demand center as China, India, and Southeast Asia expand fleets and open greenfield facilities. The Middle East continues to develop wide-body engine and heavy-check capabilities aligned with major hub carriers. Investment hotspots include Asian engine shops, digital CBM platforms, component repair clusters near high-cycle narrow-body hubs, and training academies to alleviate technician shortages.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The global Aircraft Maintenance market reached USD 85.7 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit USD 155.3 billion by 2034 (6.3% CAGR), underpinned by fleet expansion, rising utilization, and digital maintenance adoption.
- Maintenance Type (Engine): Engine MRO led with 34.2% share in 2023, reflecting high-value shop visits, LLP replacements, and the maturing installed base of new-generation turbofans; providers such as GE Aerospace, Rolls-Royce, Safran, and Lufthansa Technik anchor this value pool.
- Aircraft Type (Narrow-Body): Narrow-body aircraft accounted for 41.2% of 2023 spend, driven by high cycle frequencies on short-/medium-haul routes and LCC capacity growth, which accelerates line maintenance and quick-turn checks.
- End Use (Commercial): The Commercial segment captured 38.4% share in 2023, supported by post-pandemic traffic recovery, tight on-time performance targets, and OEM/airline power-by-the-hour (PBH) contracts stabilizing maintenance outlays.
- Driver: Structural labor demand is rising—Boeing estimates the industry will need ~600,000 maintenance technicians globally—while regulatory rigor (FAA/EASA) sustains activity and skills refresh; the FAA’s ≥16 hours of annual training per technician reinforces continuous upskilling and compliance.
- Restraint: Capacity and compliance pressures persist—~80% of maintenance tasks are regulatory-mandated, limiting scheduling flexibility, contributing to peak-season backlogs, and elevating turnaround-time (TAT) risk where hangar slots and parts availability are constrained.
- Opportunity: Net market expansion of USD 54.3 billion (2023–2034) creates headroom for investments in predictive/condition-based maintenance (CBM), component repair clusters near high-cycle narrow-body hubs, and greenfield engine shops in growth regions.
- Trend: Digitalization is scaling—AI-enabled aircraft health monitoring, digital twins, mobile e-logbooks, and smart borescopes are improving defect detection and documentation accuracy, while selective additive manufacturing for non-critical parts shortens shop cycles.
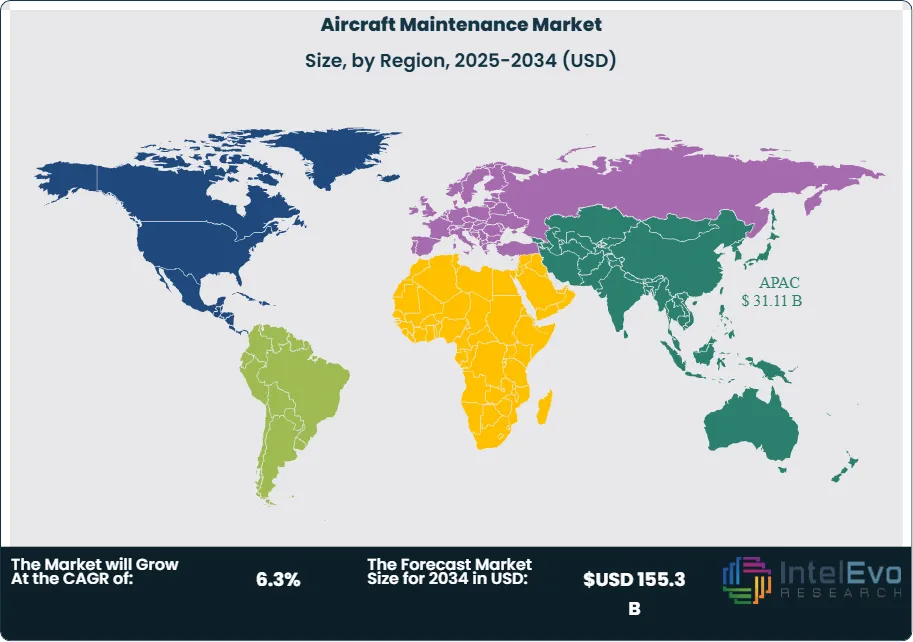
- Regional Analysis: Asia Pacific led with 36.3% share (USD 31.11 billion) in 2024, propelled by fleet additions in China, India, and Southeast Asia; North America and Europe remain large, mature bases with steady mid-single-digit growth, while the Middle East is expanding heavy-check and engine capabilities alongside hub-carrier investments.
Type Analysis
Engine services remain the economic center of aircraft maintenance, accounting for an estimated 34.2% share in 2023 and poised to expand slightly faster than the overall market through 2034 as new-generation turbofans (e.g., LEAP, GTF) move into mid-life shop cycles. Value density stems from LLP replacements, hot-section repairs, and power-by-the-hour (PBH) contracts that stabilize cash flows for airlines and MROs. The push for fuel burn and emissions reductions post-2025 is accelerating performance restorations and on-wing optimization, sustaining mid-single- to high-single-digit CAGR in engine MRO.
Line maintenance ranks second by value as high aircraft utilization and tight turnarounds keep demand elevated for fault isolation, minor repairs, and A-checks. Digital line stations using e-logbooks, e-signatures, and mobile task cards are cutting TAT and paperwork errors. Structural constraints persist: regulators drive compliance intensity—industry sources indicate ~80% of tasks are mandate-driven—while the talent gap widens; the sector anticipates a need for ~600,000 technicians globally, and annual recurrent training (e.g., ≥16 hours per FAA rules) adds time and cost but underpins safety.
Airframe heavy checks are normalizing from earlier deferrals, aided by slot additions and smarter planning tools. Components MRO—spanning avionics, actuation, landing gear, and composites—is benefiting from higher system complexity, part-out availability, and repair-instead-of-replace economics; adoption of smart borescopes, advanced NDT, and selective additive manufacturing is shortening shop cycles. “Others” (notably avionics/electrical) remains smaller but strategically critical for reliability and regulatory compliance.
Application Analysis
Narrow-bodies held 41.2% of spend in 2023 and are set to gain share through 2030 as airlines add A320neo and 737 MAX families to short-/medium-haul networks. High cycle counts translate to frequent line checks, tire/brake turns, and engine on-wing work, while PBH penetration and predictive maintenance are lifting availability and lowering unscheduled events.
Wide-bodies retain substantial value on the back of long-haul recovery and engine/landing-gear workscopes with high ticket sizes. Complexity—composite structures, advanced avionics, and ETOPS requirements—drives higher labor hours per event and a denser certification footprint, favoring tier-1 MRO hubs. The “Others” category (regional jets and turboprops) remains essential for secondary/remote routes; harsh operating environments and shorter sectors necessitate tailored component programs and robust supply-chain support.
End-Use Analysis
Commercial operators commanded 38.4% of 2023 maintenance outlays and are expected to edge above 40% by the late 2020s as fleets expand and utilization normalizes. Airlines are deepening PBH and used-serviceable-material (USM) strategies, while condition-based maintenance (CBM) and digital twins are cutting delay minutes and improving part lifecycles.
Military sustainment remains sizable, anchored by readiness mandates, life-extension programs for legacy fleets, and modernization of avionics/mission systems. Sovereign MRO capacity and parts localization are strategic priorities, supporting predictable multi-year budgets. The “Others” segment (cargo, business, charter) is growing with e-commerce air networks and elevated bizjet utilization; opportunities cluster in engine/APU overhauls, landing gear, and avionics retrofits aligned to evolving airworthiness standards.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific led with 36.3% share (USD 31.11 billion) in 2024 and is set to post the fastest growth through 2034 as China, India, and Southeast Asia add capacity, open greenfield hangars, and expand engine/component shops. Government support for aviation infrastructure and technician training will remain pivotal to alleviating slot and labor bottlenecks.
North America and Europe form the largest mature bases, supported by extensive installed fleets, strong PBH penetration, and deep tiered supplier networks. North America’s aging narrow-body cohorts sustain heavy airframe and engine shop activity, while Europe’s stringent environmental and safety regimes accelerate adoption of digital records, paperless compliance, and sustainable materials—supporting steady mid-single-digit CAGR.
The Middle East is scaling heavy-check and engine capabilities around global hub carriers, positioning for wide-body shop-visit demand. Latin America is gradually expanding capacity to support domestic growth and fleet modernization, with rising opportunities in components and landing-gear overhauls. Africa remains nascent but investable, with potential clustered around regional connectivity initiatives, parts pooling, and training academies that address chronic maintenance access gaps.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMarket Key Segments
By Maintenance Type
- Engine
- Line Maintenance
- Airframe
- Components
- Others
By Aircraft Type
- Narrow-body Aircrafts
- Wide-body Aircrafts
- Others
By End-Use
- Commercial
- Military
- Others
By Regions
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 85.7 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 155.3 B |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 6.3% |
| Historical data | 2018-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | By Maintenance Type (Engine, Line Maintenance, Airframe, Components, Others), By Aircraft Type (Narrow-body Aircrafts, Wide-body Aircrafts, Others), By End-Use (Commercial, Military, Others) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Delta TechOps, AFI KLM E&M, ST Aerospace, Pratt & Whitney, Lufthansa Technik, Honeywell International Inc., General Electric Company, GMF AeroAsia, AIRBUS |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date