Autonomous Forklift Market Size, Share & Growth Forecast 2034 | 12.9% CAGR
Global Autonomous Forklift Market Size, Share & Analysis By Product Type (AGVs, Autonomous Forklifts, Collaborative Mobile Robots), By Load Capacity (Light-Duty, Medium-Duty, Heavy-Duty), By Application (Warehousing & Logistics, Manufacturing, Retail & E-commerce Fulfillment), By End-User Industry Regions & Key Players – Automation Trends & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview:
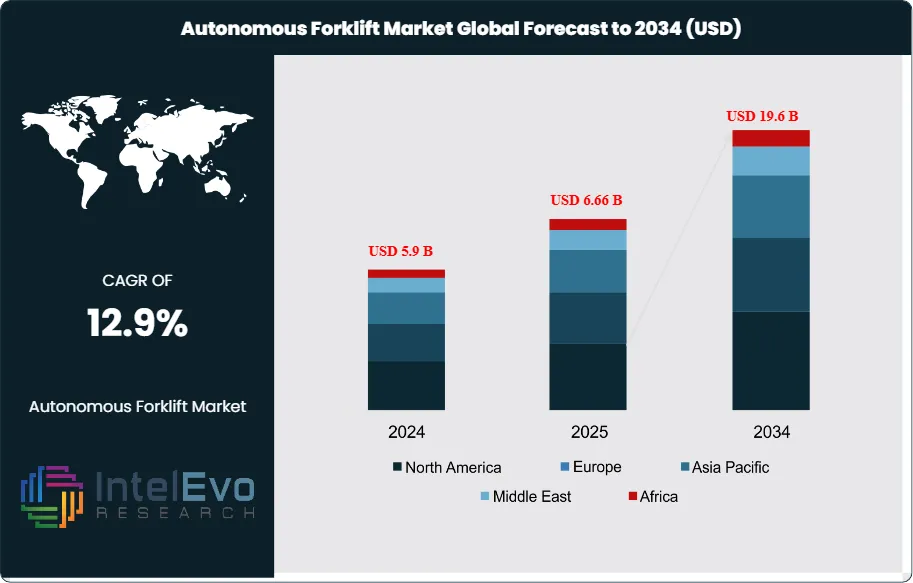
The Global Autonomous Forklift Market size is expected to be worth around USD 19.6 billion by 2034, up from USD 5.9 billion in 2024, growing at a robust CAGR of 12.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The rising adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies and the increasing need for efficient, safe, and flexible material handling systems are driving rapid market expansion. As automation continues to reshape the logistics and manufacturing sectors, autonomous forklifts are becoming essential for enhancing productivity, reducing labor costs, and ensuring workplace safety. The market is poised to witness significant innovation with the integration of AI, IoT, and advanced navigation systems.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportAn autonomous forklift is a self-driving material handling vehicle designed to transport, lift, and stack goods without direct human operation. Equipped with sensors, cameras, navigation systems, and advanced software, these forklifts can safely navigate warehouses or industrial facilities, detect obstacles, and perform tasks such as loading and unloading with minimal or no manual input. They are commonly used to improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and enhance workplace safety in logistics, manufacturing, and distribution environments.
As warehouse operations become increasingly automated, autonomous forklifts are gaining strong traction. One of the key reasons is their ability to operate continuously without the need for breaks, supervision, or concern about human fatigue. This is especially valuable in today’s logistics landscape, where there’s a shortage of skilled labor and hiring qualified forklift operators can be both challenging and costly. By automating repetitive material-handling tasks, these forklifts help reduce dependence on manual labor, cutting down overall staffing costs. Additionally, with the use of precise sensors and intelligent navigation systems, autonomous forklifts can accurately move, pick, and place goods. This leads to fewer handling errors, reduced product damage, improved inventory accuracy, and even lower insurance risks due to safer operations.
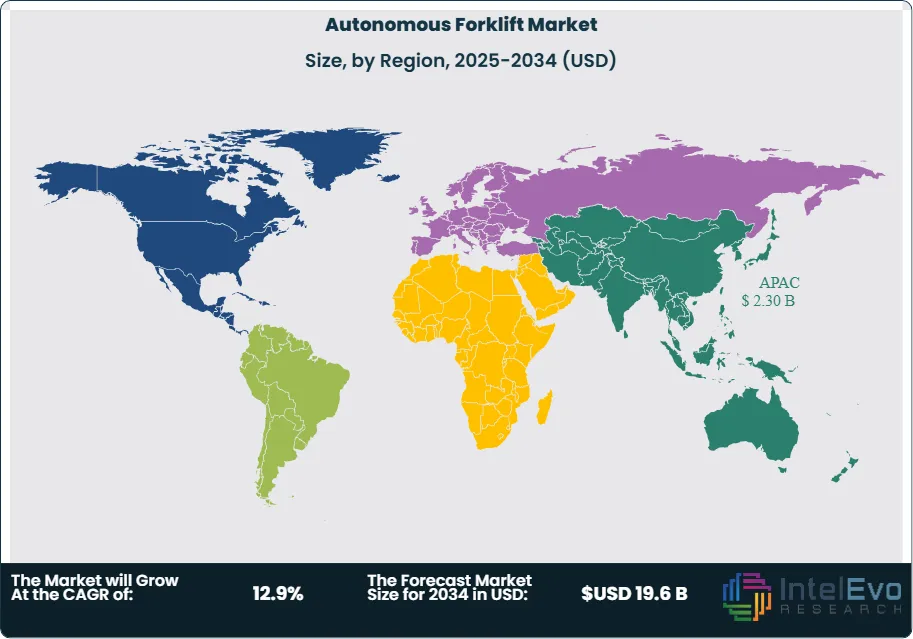
The Asia-Pacific region is emerging as a key growth hub for the autonomous forklift market, fueled by rapid industrialization, expanding e-commerce, and rising demand for efficient warehouse automation. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, and India are investing heavily in smart manufacturing and logistics infrastructure, creating a favorable environment for advanced material handling solutions. The growing labor costs and shortages in key logistics hubs across the region are also prompting businesses to turn to autonomous forklifts to maintain productivity while cutting operational expenses. Additionally, government initiatives promoting Industry 4.0 and smart factory development are further encouraging the adoption of autonomous technologies across sectors such as automotive, electronics, and retail.
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly accelerated the adoption of autonomous forklifts across various industries. As companies faced strict social distancing protocols and labor shortages due to health concerns, the need for contactless and efficient material handling became more urgent. Warehouses and distribution centers turned to automation to maintain operations with fewer on-site workers, and autonomous forklifts proved to be a practical solution. These machines helped ensure business continuity while minimizing human interaction. The pandemic also exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, prompting companies to invest in resilient and flexible automation technologies. As a result, the demand for autonomous forklifts surged and continues to grow as businesses prioritize safety, efficiency, and long-term preparedness.

Key Takeaways:
- Market Growth: The autonomous forklift market is expected to reach USD 19.6 billion by 2034, growing at a robust CAGR of 12.9%, indicating strong market expansion.
- Product Segment Dominance: The product segment is dominated by counterbalance, accounting for over 58% of the market share. Owing to their straightforward and stable design, counterbalance forklifts are easier to adapt for autonomous use. This simplicity reduces the need for extensive modifications, helping manufacturers and operators save on development time and implementation costs. As a result, deploying automated systems becomes more efficient and cost-effective.
- End-user Segment Insights: Warehouses and logistics is anticipated to hold the largest market share. Warehouses and logistics hubs often deal with repetitive tasks like picking, placing, and shipping goods. Autonomous forklifts are well-suited for these routine operations, efficiently handling them without the need for human input. This automation frees up employees to concentrate on more complex, value-added tasks and decision-making.
- Driver: The growth of e-commerce and the need for faster, more efficient logistics operations are fueling the adoption of autonomous forklifts. These machines help reduce labor costs, improve accuracy, and enhance productivity.
- Restraint: The cost of acquiring and implementing autonomous forklifts, along with the technical challenge of integrating them into existing warehouse systems, poses a major hurdle—especially for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Opportunity: Developing economies in Asia Pacific and Latin America are investing heavily in automation and logistics infrastructure. This creates significant growth potential for autonomous forklift adoption in these regions.
- Trend: Continued innovation in AI, machine vision, and sensor technologies is enhancing the navigation, obstacle detection, and safety of autonomous forklifts, making them more reliable and efficient in complex warehouse environments.
- Regional Analysis: The Asia-Pacific autonomous forklift market is witnessing strong growth due to several key factors. Rising investments in infrastructure and construction projects are increasing the demand for efficient material handling solutions. Additionally, the rapid expansion of the e-commerce and warehousing sectors across the region—especially in countries like China, India, and Southeast Asia—is driving the need for automated logistics. Autonomous forklifts are extensively used in these settings for tasks like transporting materials and loading/unloading goods. Coupled with growing industrial activities and a push for automation, these factors are fueling the adoption of autonomous forklifts in Asia-Pacific.
Product Analysis:
Autonomous forklift market can be categorized by product. These include warehouse, counterbalance, and others. Counterbalance forklifts are particularly well-suited for automation due to their inherently stable design. The built-in counterweight at the rear balances heavy loads at the front, allowing for smooth and secure lifting—an essential feature for autonomous performance. These forklifts also commonly come equipped with advanced control systems that manage key functions such as engine output, hydraulic movement, and steering precision. This makes them a strong foundation for integrating autonomous technology, as much of the necessary infrastructure for automation is already in place. The design of counterbalance forklifts lends itself well to automation, making them easier to convert compared to other forklift types. Because of their simple, stable structure, integrating autonomous features typically requires fewer modifications. This can help manufacturers and operators save both time and money by shortening development timelines and minimizing the investment needed to deploy automated systems.
End-User Analysis:
There are three categories for end-users: Chemical, food & beverage, manufacturing, logistics & warehousing, retail & e-commerce, and others. Logistics & warehousing is gaining mainstream popularity as autonomous forklifts help meet that demand by running continuously, navigating tight warehouse spaces efficiently, and reducing the chance of errors—ultimately improving turnaround times and streamlining operations.. In today’s fast-paced warehouse and logistics environments, tasks like moving goods, stacking pallets, and retrieving inventory are repeated constantly. Autonomous forklifts are well-suited for these kinds of jobs, handling them smoothly without the need for constant supervision. This lets staff shift their attention to more specialized work that requires judgment or problem-solving. As online shopping continues to surge, so does the pressure to deliver orders quickly and accurately.
Region Analysis:
Asia Pacific Leads With 39% Market Share in the Autonomous Forklift Market: The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing significant momentum in the adoption of autonomous forklifts, fueled by a combination of industrial expansion, technological advancements, and the growing need for operational efficiency in logistics and warehousing. Countries such as China, Japan, South Korea, and India are leading this trend, each driven by unique but complementary factors. For instance, China’s focus on developing smart factories under the “Made in China 2025” initiative, along with its booming e-commerce sector, has pushed logistics providers and manufacturers to embrace automation technologies like autonomous forklifts to keep pace with demand and reduce labor dependency. Moreover, the presence of global and regional players investing in R&D and collaborating with local tech firms is helping accelerate the adoption of autonomous forklift technology. As companies across the Asia-Pacific region aim to modernize supply chains, minimize downtime, and respond quickly to shifting consumer expectations, autonomous forklifts are becoming an integral part of the smart logistics ecosystem.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample Report
Key Market Segment
By Product Type
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
- Autonomous Forklifts
- Collaborative Mobile Robots
By Load Capacity
- Light-Duty (up to 2 tons)
- Medium-Duty (2–5 tons)
- Heavy-Duty (>5 tons)
By Application
- Warehousing & Logistics
- Manufacturing
- Retail & E-commerce Fulfillment Centers
- Food & Beverage Industry
- Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
- Others
By End-User Industry
- Automotive
- FMCG & Retail
- E-commerce
- Electronics & Semiconductors
- Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2025) | USD 6.66 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 19.6 B |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 12.9% |
| Historical data | 2018-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | By Product Type (Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Autonomous Forklifts, Collaborative Mobile Robots), By Load Capacity (Light-Duty (up to 2 tons), Medium-Duty (2–5 tons), Heavy-Duty (>5 tons)), By Application (Warehousing & Logistics, Manufacturing, Retail & E-commerce Fulfillment Centers, Food & Beverage Industry, Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare, Others), By End-User Industry (Automotive, FMCG & Retail, E-commerce, Electronics & Semiconductors, Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals, Others) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | BlueBotics SA, EK Automation GmbH, Jungheinrich AG, Seegrid Corporation, Yale Materials Handling Corporation, Balyo SA, Daifuku Co., Ltd., Hyster-Yale Materials Handling, Inc., KION Group, Toyota Industries Corporation, Crown Equipment Corporation, Mitsubishi Logisnext Co., Ltd., Linde Material Handling (KION Group), Nissan Forklift Corporation, Anhui Heli Co., Ltd., Raymond Corporation, Clark Material Handling Company, UniCarriers Corporation |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date