Carpooling Apps Market Size, Share $34.26 Bn by 2034 | 10.81% CAGR
Global Carpooling Apps Market Size, Share, Analysis Report Type of Routes (Dynamic Carpooling, Fixed-Route Carpooling, Slugging),Vehicle Capacity (Vans, Small Cars, Mid-Size Cars), Distance Range (Long-Distance, Short-Distance, Medium-Distance), Commuter Frequency( Occasional Commuters, Daily Commuters, Weekly Commuters) Industry Region & Key Players-Industry Segment Overview, Market Dynamics, Competitive Strategies, Trends & Forecast 2025-2034
Report Overview
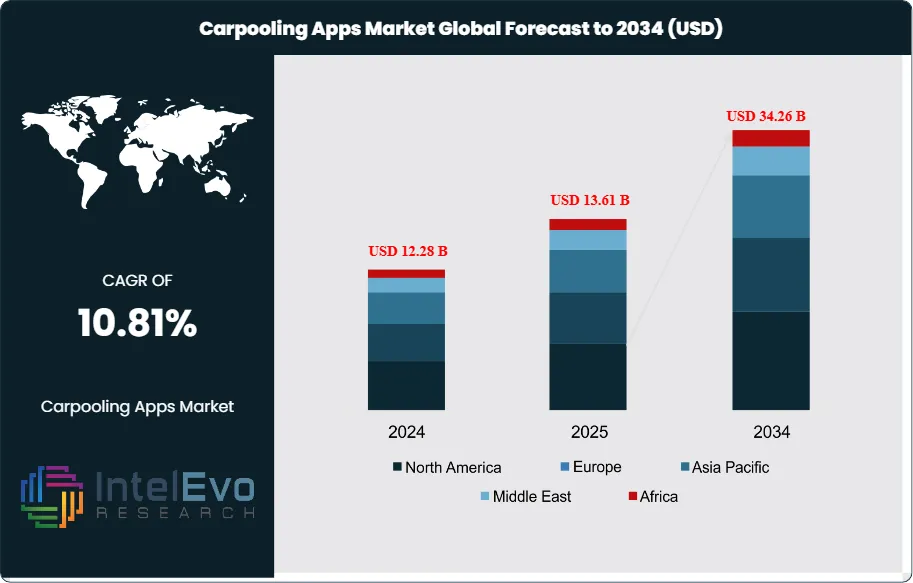
The Carpooling Apps Market size is expected to be worth around USD 34.26 billion by 2034, up from USD 12.28 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 10.81% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2034. This strong growth is driven by increasing urban congestion, rising fuel costs, and growing consumer preference for cost-effective and environmentally sustainable mobility solutions. Rapid smartphone penetration, integration of AI-based route optimization, and government support for shared mobility initiatives are further accelerating adoption, positioning carpooling apps as a critical component of the evolving smart transportation ecosystem worldwide.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportThe carpooling apps market represents a rapidly expanding segment within the broader shared mobility ecosystem, facilitating ride-sharing solutions through digital platforms that connect drivers with passengers traveling similar routes. The market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating expansion from USD 9.64 billion in 2023 to USD 34.2 billion by 2034, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.9-11.9%. Key factors driving this market expansion include escalating fuel costs, increasing urbanization, growing environmental consciousness, and the need for cost-effective transportation solutions. The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, GPS tracking, real-time matching algorithms, and mobile payment systems has revolutionized the user experience, making carpooling more accessible and efficient than traditional transportation methods.
The market dynamics are influenced by several critical factors including regulatory frameworks, smartphone penetration rates, internet connectivity, and changing consumer preferences toward sustainable transportation alternatives. Government initiatives promoting shared mobility to reduce traffic congestion and carbon emissions further accelerate market adoption. Additionally, the rise of smart cities and the implementation of congestion pricing in urban areas create favorable conditions for carpooling services growth.
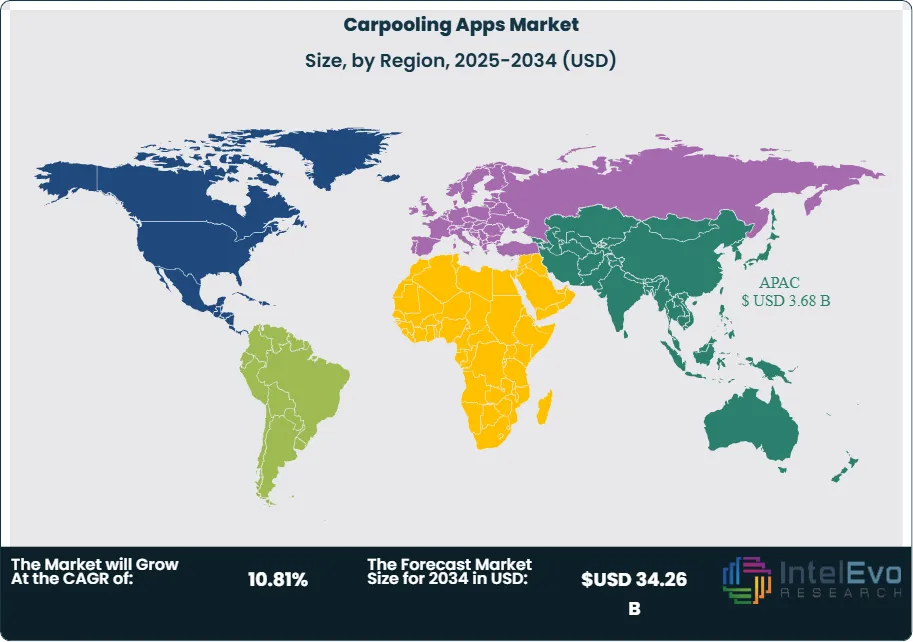
The Asia-Pacific region dominates the global carpooling market, accounting for the largest market share in 2023, driven by rapid urbanization, increasing traffic congestion, and growing environmental concerns. The region's large population density, rising middle-class income levels, and high smartphone adoption rates create optimal conditions for carpooling platform growth. Western Europe represents the second-largest market, followed by North America, with emerging markets in South America and Africa showing significant potential for future expansion.
The COVID-19 pandemic initially created substantial challenges for the carpooling apps market, with widespread lockdowns, travel restrictions, and health safety concerns leading to dramatic reductions in ride-sharing activities during 2020-2021. Social distancing protocols and hygiene concerns significantly impacted user confidence in shared transportation services. However, the market demonstrated remarkable resilience and adaptability, with companies implementing enhanced safety protocols, contactless payment systems, and vehicle sanitization measures. The post-pandemic recovery phase has shown accelerated adoption as economic recovery drives mobility demand, while environmental awareness continues to promote shared transportation solutions.
Ongoing regional conflicts and trade tensions between major economies have created complex impacts on the carpooling apps market through supply chain disruptions, technology transfer restrictions, and regulatory uncertainties. The US-China trade tensions have affected technology partnerships and data sharing agreements, while geopolitical conflicts in Europe and other regions have influenced fuel prices and transportation patterns. Tariffs on automotive components and technology imports have increased operational costs for carpooling platforms, particularly affecting electric vehicle integration initiatives. However, these challenges have also accelerated localization efforts and fostered innovation in regional markets, creating opportunities for domestic players to compete with global giants. The ongoing conflicts have heightened the importance of energy independence and sustainable transportation solutions, potentially accelerating carpooling adoption as governments seek to reduce fuel import dependencies.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Carpooling Apps Market is expected to reach USD 34.26 Billion by 2034, driven by urbanization, digital innovation, cost-efficiency, and sustainability priorities.
- Type of Routes Dominance: Dynamic carpooling leads the market through its flexible, on-demand matching capabilities that optimize route efficiency and passenger convenience. This segment benefits from advanced AI algorithms that provide real-time matching and dynamic pricing models.
- Vehicle Capacity Dominance: Small cars represent the dominant vehicle capacity segment due to their optimal balance of passenger capacity, fuel efficiency, and urban maneuverability. These vehicles offer cost-effective solutions for daily commuting while maintaining comfortable passenger experiences.
- Distance Range Dominance: Short-distance carpooling dominates the market by addressing the most frequent transportation needs within urban and suburban areas. This segment benefits from high trip frequency, quick turnaround times, and integration with daily commuting patterns, making it the most utilized distance category.
- Commuter Frequency Dominance: Daily commuters constitute the largest user segment, driving consistent demand through regular work-related transportation needs. This segment generates predictable revenue streams and benefits from subscription-based pricing models and route optimization.
- Driver: Urban congestion, rising fuel costs, sustainability goals, and corporate commuting programs are key growth drivers.
- Restraint: Vehicle cost spikes due to tariffs hinder driver onboarding; safety concerns, technology costs, and consumer adoption also act as barriers.
- Opportunity: Corporate and public sector partnerships (CaaS integration), AI-powered dynamic routing, and underserved markets in emerging APAC and Latin America offer growth.
- Trend: Integration with mass transit, super-app expansion in Southeast Asia, electric/autonomous vehicle carpooling, and tech-led ride-matching.
- Regional Analysis: Asia-Pacific maintains market leadership due to high population density, rapid urbanization, and supportive government policies promoting shared mobility solutions. The region's tech-savvy population and smartphone penetration create ideal conditions for app-based transportation services adoption.
Type of Routes Analysis:
Slugging Leads With more than 45% Market Share In Carpooling Apps Market. Slugging represents the most established and cost-effective form of carpooling, particularly dominant in major metropolitan areas where traffic congestion and high-occupancy vehicle (HOV) lane access create significant advantages. This informal carpooling system operates on a first-come, first-served basis at designated pickup locations, eliminating the need for advance planning or technology-mediated matching. Slugging's popularity stems from its simplicity and mutual benefits - drivers gain access to HOV lanes for faster commutes, while passengers receive free or low-cost transportation. The system thrives in regions with well-established business districts and predictable commuting patterns, creating organic networks of regular participants. Major cities like Washington D.C., San Francisco, and Seattle have developed extensive slugging communities with established etiquette, pickup locations, and informal safety protocols. The segment's growth is driven by increasing traffic congestion, rising fuel costs, and environmental consciousness, while its limitations include weather dependency, limited flexibility, and challenges in scaling to new markets without existing infrastructure.
Vehicle Capacity Analysis:
The small cars segment dominates the vehicle capacity category due to its optimal combination of passenger accommodation, fuel efficiency, and urban navigation capabilities. These vehicles represent the sweet spot for most carpooling scenarios, providing sufficient space for typical group sizes while maintaining economic viability for drivers. Small cars offer superior maneuverability in congested urban environments, easier parking accessibility, and lower operational costs including fuel consumption, maintenance, and insurance compared to larger vehicles. The segment benefits from the widespread availability of compact and mid-size vehicles in global automotive markets, making it accessible for potential drivers without requiring specialized vehicle investments. Modern small cars increasingly feature advanced safety systems, comfortable interiors, and connectivity features that enhance the carpooling experience. The segment's dominance is reinforced by regulatory preferences in many jurisdictions that classify small-car carpooling as ride-sharing rather than commercial transportation, reducing compliance burdens for participants.
Distance Range Analysis:
Short-distance carpooling dominates the market by addressing the most frequent transportation needs within urban and suburban areas, capturing the largest share of daily commuting and local travel demand. This segment benefits from high trip frequency, quick turnaround times, and minimal time commitments that appeal to both drivers and passengers seeking flexible transportation solutions. Short-distance trips align perfectly with urban density patterns, connecting residential areas with business districts, shopping centers, and transit hubs within metropolitan regions. The segment's success stems from its integration with daily routines, offering convenient solutions for regular errands, work commutes, and social activities without requiring significant time investments. Technology platforms optimized for short-distance carpooling focus on rapid matching, minimal waiting times, and efficient route optimization within limited geographic areas. The segment faces unique challenges including lower per-trip revenues that require high volume to achieve profitability, competition from public transportation and micromobility options, and the need for dense user networks to ensure reliable service availability.
Commuter Frequency Analysis:
Daily commuters constitute the backbone of the carpooling apps market, generating consistent demand patterns that enable platforms to build predictable business models and optimize resource allocation. This segment includes professionals traveling to fixed workplaces on regular schedules, creating opportunities for recurring carpooling arrangements and long-term passenger-driver relationships that enhance trust and reliability. Daily commuters represent the most valuable user segment due to their predictable travel patterns, higher lifetime value, and reduced customer acquisition costs through established routines. The segment benefits from employer partnerships, corporate transportation programs, and subscription-based pricing models that provide cost predictability for users and revenue stability for platforms. Daily commuters appreciate the social aspects of regular carpooling relationships, environmental benefits of reduced individual vehicle use, and potential cost savings compared to vehicle ownership, parking fees, and public transportation passes. Platform features targeting this segment include advance booking systems, recurring ride scheduling, preferred driver matching, and integration with corporate expense management systems to streamline the commuting experience.
Region Analysis:
Asia-Pacific Leads With nearly 30% Market Share In Carpooling Apps Market. The Asia-Pacific region leads the global carpooling apps market, capturing the largest market share due to rapid urbanization, increasing traffic congestion, and supportive government environmental policies. Countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations drive this dominance through massive urban populations, rising smartphone adoption, and growing environmental awareness. The region's dense population centers create ideal conditions for carpooling services, while relatively lower average incomes make cost-sharing attractive to consumers.
Western Europe represents the second-largest market, characterized by strong environmental regulations, high fuel costs, and mature digital infrastructure. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK lead adoption through supportive regulatory frameworks and corporate sustainability initiatives. North America shows steady growth despite higher individual vehicle ownership rates, driven by urban congestion and environmental consciousness in major metropolitan areas.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportKey Market Segment
Type of Routes
- Dynamic Carpooling
- Fixed-Route Carpooling
- Slugging
Vehicle Capacity
- Vans (10+ seats)
- Small Cars (4-6 seats)
- Mid-Size Cars (7-9 seats)
Distance Range
- Long-Distance (50+ miles)
- Short-Distance (less than 10 miles)
- Medium-Distance (10-50 miles)
Commuter Frequency
- Occasional Commuters
- Daily Commuters
- Weekly Commuters
Region
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2025) | USD 13.61 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 34.26 B |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 10.81% |
| Historical data | 2018-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | Type of Routes (Dynamic Carpooling, Fixed-Route Carpooling, Slugging) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Hailo, Getaround, Turo, Green Pea, Car2Go, Via, Maven, Uber, Bridj, Lyft, Zipcar, BlaBlaCar, ReachNow, moovel, mytaxi |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date