CNC Machines Market Forecast Growth, Trends & Insights | 10.8% CAGR
Global CNC Machines Market Size, Share & Analysis By Machine Type (Lathe, Milling, Grinding, EDM), By Axis Type (3-Axis, 4-Axis, 5-Axis), By End-User (Automotive, Aerospace, Industrial Manufacturing) Industry Regions & Key Players – Smart Factory Trends & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
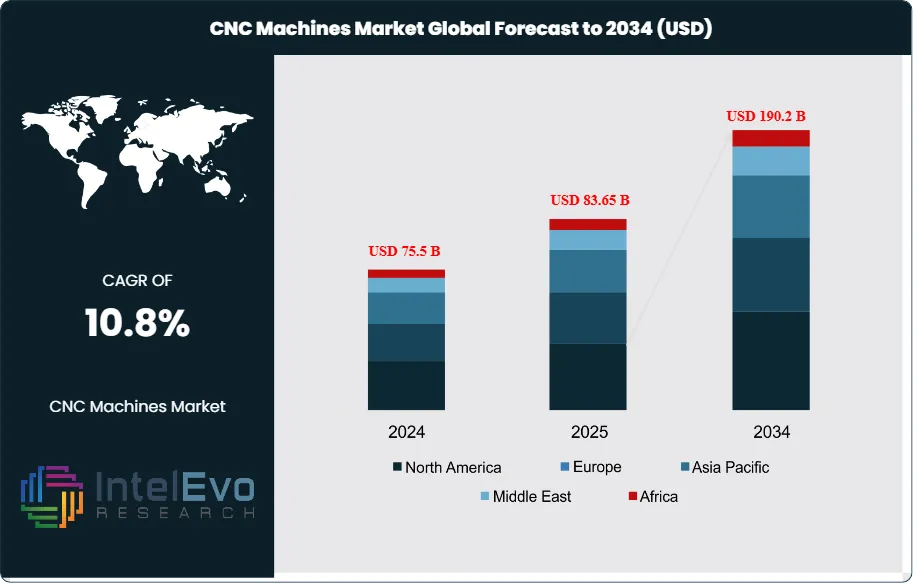
The CNC Machines Market is estimated at USD 75.5 billion in 2024 and is on track to reach roughly USD 190.2 billion by 2034, implying a compound annual growth rate of 10.8% over 2024–2034. Momentum reflects a structural shift toward automated, high-precision manufacturing as producers confront rising labor costs, tighter tolerances, and accelerating product refresh cycles. After a steady expansion in the last five years—supported by automotive retooling, aerospace backlog recovery, and medical device miniaturization—growth is expected to broaden from new equipment to lifecycle revenues, with services, retrofits, and software subscriptions accounting for a rising share of spend by 2030.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportOn the demand side, plants operating at only 60–80% overall equipment effectiveness are adopting CNC to lift first-pass yield and reduce scrap; deployments typically improve throughput 10–15%, cut material waste by 8–12%, and shorten set-up times by up to 30%, directly enhancing unit economics. On the supply side, OEMs are compressing lead times through modular platforms and localized assembly, while competition on price/performance is intensifying in mid-range vertical machining centers and turning centers. Policy tailwinds—Industry 4.0 incentives, tax depreciation for capital equipment, and energy-efficiency standards—are reinforcing adoption, although cyclicality in capital expenditure, skills shortages for programming and metrology, and cybersecurity risks in connected factories remain key constraints.
Technology is reshaping value capture: multi-axis (5-axis) and mill-turn machines are set to outgrow the market, aided by AI-optimized toolpaths, digital twins for process verification, and edge analytics for predictive maintenance; users report 5–10% gains in spindle uptime and 10–20% extensions in tool life when analytics are embedded. Additive–subtractive hybrids are emerging for high-mix, low-volume parts, while automated pallet systems and collaborative robots expand lights-out machining.
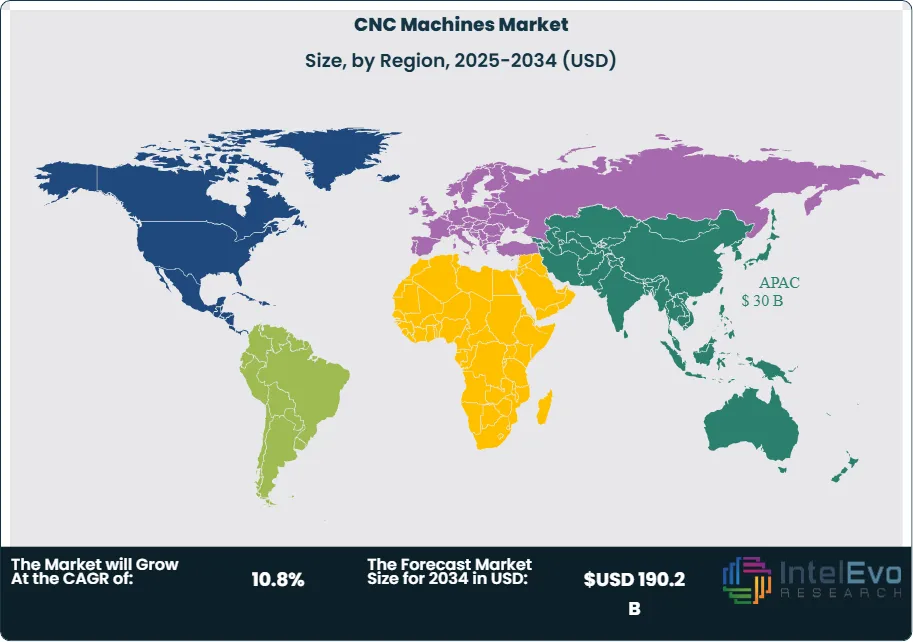
Regionally, Asia–Pacific is the volume engine (≈50% of demand), led by China’s electronics and machinery clusters and Japan/Korea’s premium machine tool ecosystems; Europe remains strong in high-precision niches (Germany, Italy) aligned to EV and aerospace programs; North America is buoyed by reshoring, semiconductor fabs, and defense orders; and investment hotspots are forming in India, ASEAN, Mexico, and Central/Eastern Europe as OEMs pursue China-plus-one and nearshoring strategies. For investors, platforms with scalable software, strong service networks, and automation-ready portfolios are positioned to capture disproportionate value through the cycle.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The CNC Machines Market was USD 73.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 190.2 billion by 2034 (10.8% CAGR), creating an incremental opportunity of USD 113.7 billion driven by factory automation, tighter tolerances in EV/aerospace, and Industry 4.0 investments.
- Segment Dominance – Product Type: Lathe/turning machines led in 2024 with 30% share (~USD 22.1 billion), reflecting their versatility for high-throughput metal and wood turning across job shops and general engineering; vendors such as Mazak, Okuma, and Haas sustain leadership through broad portfolios and competitive total cost of ownership.
- Segment Dominance – End Use: Industrial applications accounted for 27% of 2024 revenue (~USD 19.8 billion), driven by precision machining in automotive components, general machinery, and contract manufacturing, where CNC adoption reduces scrap and rework and supports high-mix, low-volume runs.
- Driver: Productivity economics are compelling as plants operating at 60–80% OEE deploy CNC to lift first-pass yield; typical programs deliver 10–15% throughput gains, 8–12% scrap reduction, and up to 30% shorter setup times, accelerating payback.
- Restraint: High capital intensity and skills scarcity constrain SME adoption—multi-axis/mill-turn cells often require USD 0.3–1.0 million per line plus integration, while shortages of CNC programmers and metrology talent elongate ramp-up timelines and increase commissioning costs.
- Opportunity: Fastest growth is expected in 5-axis and mill-turn platforms—supported by lights-out cells and pallet automation—outpacing the market as users consolidate operations on fewer machines; this, alongside retrofit/control upgrades, targets a sizeable share of the USD 113.7 billion decade-long upside.
- Trend: Digitalized machining is scaling as AI-optimized toolpaths, digital twins, and edge analytics lift spindle uptime by 5–10% and extend tool life by 10–20%; ecosystems from Siemens (Sinumerik), FANUC, and Sandvik Coromant are embedding software, connectivity, and MTConnect-ready monitoring into standard workflows.
- Regional Analysis: Asia Pacific dominated in 2024 with 37% share (≈USD 27.2 billion), led by electronics/machinery clusters in China and advanced machine tool ecosystems in Japan/Korea; North America benefits from reshoring, semiconductor fabs, and defense, while Europe retains strength in precision niches (Germany/Italy) and emerging hotspots include India, ASEAN, Mexico, and CEE.
Type Analysis
Lathe machines remain the anchor of CNC demand in 2025, accounting for roughly 30% of revenue (≈USD 24–25 billion on a market base of ~USD 80.7 billion). Their dominance stems from unmatched versatility in turning cores, shafts, and housings across steel and aluminum, with multi-turret and live-tool configurations compressing cycle times for high-mix, low-volume work. Tier-one portfolios from Mazak, Okuma, DMG MORI, and Haas continue to win on total cost of ownership, while retrofit controls extend the installed base’s productive life. Milling machines form the second-largest pool and are set to outgrow legacy three-axis platforms as 5-axis and mill-turn architectures consolidate operations; adopters report 10–15% throughput gains and up to 30% faster changeovers when pallet automation is integrated.
Laser machines are scaling fastest in sheet-metal and precision profiling, aided by fiber sources, automated loading, and nesting software that lifts material utilization. The segment is expected to grow in the low-teens CAGR through 2030 as TRUMPF/Bystronic-class systems migrate downstream to job shops. CNC welding solutions—coordinated robots with seam-tracking and real-time quality monitoring—capture 5–7% share, driven by EV chassis, agricultural equipment, and heavy fabrications. Winding machines, though niche (3–4% share), benefit from electrification tailwinds in motors, e-axles, and transformers. “Other” types—grinders, EDM, routers—collectively address high-precision finishing and composites, sustaining 15–18% of spend as tolerance requirements tighten.
Application Analysis
Production machining for precision components remains the largest application cluster (≈55–60% of 2025 revenue), spanning powertrain housings, hydraulic blocks, and aerospace fittings. Plants operating at 60–80% OEE are prioritizing CNC upgrades to boost first-pass yield; typical programs cut scrap 8–12% and extend tool life 10–20% with adaptive feeds and in-process metrology. Sheet-metal fabrication is a second growth engine as white-goods, EV body parts, and industrial enclosures shift to fiber-laser cuts and automated bending cells, with laser systems now representing about a quarter of new installations in many job-shop districts.
Prototyping, tooling, and mold/die work are increasingly digital, leveraging CAD/CAM-driven 5-axis rough-to-finish strategies and hybrid additive–subtractive cells to compress development cycles. Early adopters report 20–30% shorter time-to-tool and measurable reductions in rework via simulation and digital twins. Micro-machining for medical and electronics, while smaller in absolute terms, posts outsize growth as miniaturization and surface-finish requirements intensify.
End-Use Analysis
General industrial and contract manufacturing remains the single largest end-use, near 26–28% of 2025 revenue (≈USD 22 billion), reflecting broad deployment across machinery, job shops, and metal fabrication. Automotive demand is pivoting from legacy ICE machining to EV platforms: battery trays, e-motor shafts, and inverter housings favor multi-axis milling and high-speed aluminum cutting, with automation driving unattended shifts. Aerospace & defense continues to outpace the market on complex geometries and superalloys; 5-axis penetration is highest here, supported by closed-loop probing and toolpath optimization to safeguard part integrity on long cycle times.
Construction equipment and off-highway machinery rely on heavy-duty turning/milling and robotic welding, growing broadly in line with the market as infrastructure spending normalizes. Power & energy posts high single- to low double-digit growth on gas-turbine components, grid hardware, and wind drivetrain parts, where precision and reliability standards are stringent. “Other end-users”—medical devices and consumer electronics—are expanding fastest off a smaller base, propelled by micro-features, tight tolerances, and validated process control.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific retains leadership in 2025 with ~37% share (≈USD 30 billion), underpinned by China’s electronics and machinery clusters, Japan/Korea’s premium machine-tool ecosystems, and accelerating capacity additions in India and ASEAN. Localization policies and Industry 4.0 incentives are lifting adoption of automation-ready cells and domestic control platforms. Europe remains a high-precision stronghold (Germany, Italy, Switzerland) aligned to aerospace, automotive tooling, and medical machining; despite energy-cost headwinds, the region sustains an advanced installed base and deep process know-how. North America is buoyed by reshoring, semiconductor fabs, and defense procurement, with robust demand for palletized 5-axis cells and MTConnect-ready monitoring.
Emerging hotspots include India, Mexico, Vietnam, and Central & Eastern Europe, each benefiting from “China-plus-one” and near-shoring strategies. These markets are expected to compound at double-digit rates through the late 2020s as suppliers build local machining capacity and integrators expand service networks. Investors should track regions pairing capital incentives with skilled-labor pipelines, as aftersales and software subscriptions increasingly shape lifetime economics.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMarket Key Segments
By Type
- Lathe Machines
- Milling Machines
- Laser Machines
- Welding Machines
- Winding Machines
- Other Types
By End-User
- Automotive
- Aerospace & Defense
- Construction Equipment
- Power & Energy
- Industrial
- Other End-Users
Regions
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 75.5 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 190.2 B |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 10.8% |
| Historical data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | By Type (Lathe Machines, Milling Machines, Laser Machines, Welding Machines, Winding Machines, Other Types), By End-User (Automotive, Aerospace & Defense, Construction Equipment, Power & Energy, Industrial, Other End-Users) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Hurco Companies, Inc., Shenyang Machine Tool Part Co., Ltd., Okuma Corporation, General Technology Group, Haas Automation, Inc., Fanuc Corporation, Yamazaki Mazak Corporation, Amada Machinery Co., Ltd., Dalian Machine Tool Corporation, Amera Seiki, DMG Mori Co., Ltd., Datron AG |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date