Defense Cybersecurity Market Size & Threat Outlook | 17.2% CAG
Global Defense Cybersecurity Market Size, Share & Analysis By Component (Software and Services, Hardware), By Solution Type (Cyber Threat Protection, Content Security, Threat Evaluation, Other Solution Types), By Application (Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience, Cloud Security, Application Security, Other Applications), By End-User (Land Force, Naval Force, Air Force) Industry Outlook, Risk Landscape, Technology Roadmap, Key Players & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
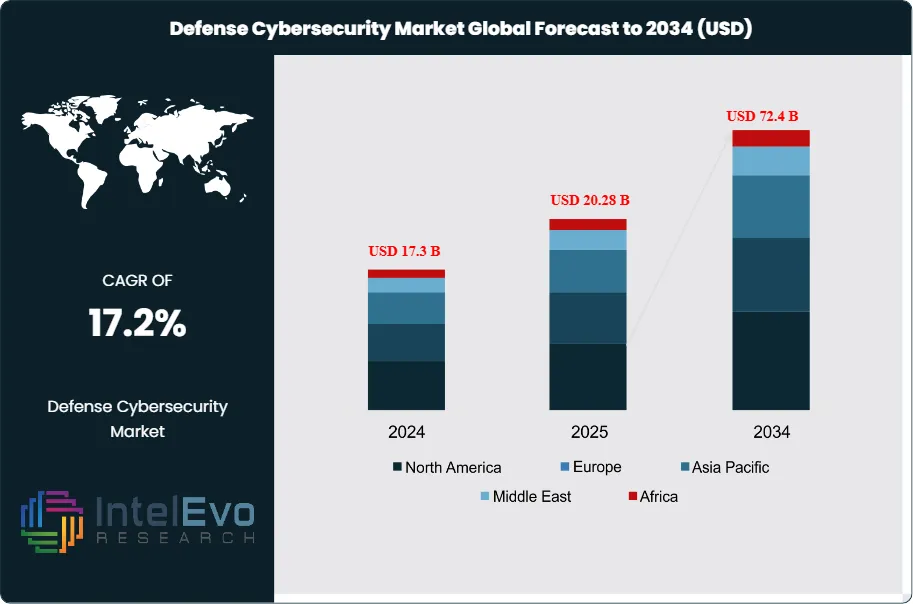
The Defense Cybersecurity Market was valued at approximately USD 17.3 Billion in 2024 and is expected to reach nearly USD 72.4 Billion by 2034, growing at an estimated CAGR of about 17.2% from 2025 to 2034. Nation-states are increasing defense budgets to counter evolving cyber warfare, AI-driven attacks, and critical infrastructure vulnerabilities. The rise of autonomous systems, battlefield digitalization, and real-time threat intelligence is accelerating demand for advanced military-grade cybersecurity.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportThe next decade marks a high-security investment cycle, making defense cyber capabilities a top global priority. This upward trajectory reflects growing urgency among nations to defend against increasingly complex cyber threats posed by both state and non-state actors.
Traditional, perimeter-based cybersecurity frameworks are proving inadequate as digital warfare evolves. Modern military operations now demand proactive, intelligence-led defenses. For context, in 2024 alone, there were over 800,000 global cyberattacks, with 300 specifically targeting defense agencies and an additional 500 directed at related government institutions.
Multiple forces are fueling this expansion. Rising geopolitical tensions, deeper digital integration in military systems, and a broader attack surface are pushing defense bodies to upgrade their cybersecurity strategies. For instance, the U.S. Department of Defense’s “Defend Forward” strategy is designed to disrupt potential cyber threats before they strike. Simultaneously, many militaries are dealing with legacy infrastructure and a significant shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals—challenges that have accelerated demand for automation and AI-powered solutions.
Emerging technologies, especially AI and machine learning, are now central to this transformation. They allow faster threat detection, real-time responses, and automated incident remediation. Reflecting this shift, the 2024 U.S. National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) allocated part of its $857.9 billion budget to AI and cybersecurity development. Similar investments are being seen globally—for instance, Australia’s $9.9 billion REDSPICE program.
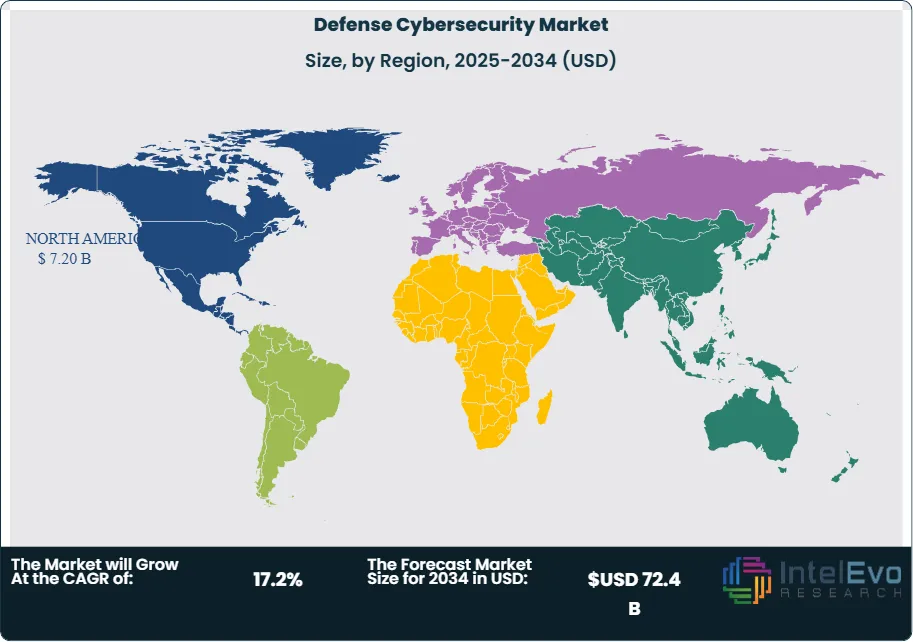
North America remains the largest market, backed by advanced infrastructure and significant defense spending. Meanwhile, the Asia-Pacific region is rapidly catching up, with countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations investing heavily in cyber-resilience. Europe is also making strides through NATO-aligned frameworks aimed at building collaborative cyber defense capabilities.
As cyberwarfare becomes more asymmetric, the demand is rising for flexible, scalable, and mission-specific cybersecurity tools. Vendors offering AI-integrated platforms, secure communications, and tailored defense solutions are well-positioned to benefit from this evolving landscape.

Key Takeaways
- Market Outlook: The defense cybersecurity market is projected to grow from USD 17.3 billion in 2024 to USD 72.4 Billion by 2034, driven by escalating cyber threats and increased digitalization of defense systems.
- Top Component: Software and services made up 60.5% of the market in 2024, driven by rising demand for dynamic threat detection tools, secure communications, and customizable cyber architecture.
- Leading Solution: Cyber Threat Protection held a 35.8% market share, reflecting heightened focus on endpoint security, threat intelligence, and next-gen firewalls.
- Dominant Application Area: Application Security accounted for 36.9% of demand, underscoring its role in safeguarding critical command-and-control systems and mission-specific software.
- Market Drivers: A key driver is the surge in high-complexity cyberattacks, including over 300 direct attacks on military targets in 2024. Programs like the U.S. DoD’s “Defend Forward” emphasize early threat intervention.
- Key Challenges: The sector continues to grapple with a shortage of cybersecurity talent and dependence on aging digital infrastructure, both of which slow modernization efforts.
- Growth Opportunities: Integrating AI and ML into cybersecurity platforms opens new avenues for automated threat response and predictive security frameworks. Government support, like the 2024 NDAA, is catalyzing this shift.
- Notable Trends: There’s a clear move toward zero-trust architectures and automated defense systems, with military institutions increasingly investing in real-time analytics and AI-based diagnostics.
- Regional Highlights: North America led in 2024 with 41.6% market share due to its strong digital defense posture. Asia-Pacific is forecasted to grow fastest, fueled by defense upgrades and rising cyber capabilities in India, China, and across Southeast Asia.
Component Analysis
As of 2025, the Software and Services segment continues to dominate the global defense cybersecurity market, accounting for approximately 60.5% of the total market share. This commanding position reflects the critical need for dynamic software capabilities and expert services that can adapt to the rapidly evolving threat landscape. Cybersecurity in the defense sector is no longer static; it requires real-time monitoring, automated threat response, and continuous system updates—all of which are enabled through advanced software tools and ongoing professional support.
Software solutions remain indispensable for delivering core cybersecurity functionalities such as next-generation firewalls, endpoint detection and response (EDR), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). Equally vital are managed services—such as cybersecurity consulting, system integration, threat intelligence, and compliance management—which enable defense agencies to optimize their security posture. With cyberattack frequency and complexity on the rise, the demand for highly specialized, mission-ready services is expected to intensify through 2034.
Although hardware comprises a smaller share of the market, its role is foundational. Devices such as secure servers, encrypted routers, and physical firewalls provide the infrastructure backbone for all cyber defense operations. Hardware's significance lies in its capacity to deliver resilient, tamper-proof environments that protect mission-critical systems from both digital and physical compromise.
Solution Type Analysis
Cyber Threat Protection leads the solution type segment, representing around 35.8% of total market value. Its leadership is driven by the urgent need to detect, neutralize, and recover from advanced persistent threats (APTs) targeting military networks and command structures. This segment encompasses multi-layered defenses, including behavioral analytics, zero-trust architecture, and AI-powered threat hunting tools—critical elements in modern cyber warfare defense strategies.
With defense systems increasingly exposed to zero-day exploits and state-sponsored cyber aggression, Cyber Threat Protection has become a top priority in military cybersecurity planning. Its real-time response capabilities help ensure operational continuity across mission-critical environments.
Supporting solution segments such as Content Security and Threat Evaluation play key roles in comprehensive defense cybersecurity strategies. Content Security ensures classified and mission-sensitive data remains uncompromised across digital channels, while Threat Evaluation tools deliver risk assessments and simulate cyberattacks to identify system vulnerabilities. Together, these solutions provide a robust, multilayered security framework aligned with the operational demands of defense organizations.
By Application Analysis
Application Security dominates this segment with a market share of 36.9%, reflecting its vital role in safeguarding the software platforms that underpin command and control systems, intelligence platforms, and mission management tools. As military operations become increasingly reliant on digital infrastructure, securing these software environments against code injections, API vulnerabilities, and unauthorized access is paramount.
This subsegment has gained momentum due to the proliferation of custom-built defense applications and increased use of mobile and cloud-native tools in field operations. Ensuring application integrity is critical not only for operational success but also for national security, particularly in multi-domain combat environments.
Complementary applications—such as Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience and Cloud Security—are witnessing increased adoption. As defense organizations migrate to hybrid IT environments, cloud platforms must be fortified with end-to-end encryption, secure access controls, and container security. Meanwhile, critical infrastructure protection remains central to cyber defense strategies, particularly for safeguarding surveillance systems, logistics networks, and defense communication nodes.
End-User Analysis
The Land Force segment represents the largest share of the defense cybersecurity market, contributing approximately 46.0% as of 2025. Ground operations involve vast, decentralized networks that integrate GPS systems, tactical communications, surveillance, and unmanned vehicles—all of which are prime targets for cyber exploitation. This high dependency on digital systems necessitates comprehensive cybersecurity frameworks to ensure operational continuity in volatile and hostile environments.
Land forces worldwide are increasingly deploying AI-driven threat detection systems, battlefield network encryption, and secure mobile command platforms. These enhancements are critical as modern conflicts become more asymmetric and technologically driven.
Naval and Air Forces, while accounting for smaller portions of the market, are advancing rapidly in terms of cybersecurity investments. Naval operations require resilient cyber defenses for shipborne systems, maritime communication networks, and underwater surveillance platforms. Similarly, Air Forces focus on securing airborne command systems, ground-based radar, and space assets. Cross-domain interoperability demands integrated cybersecurity strategies across all military branches.
Regional Analysis
North America continues to lead the global defense cybersecurity market with a commanding 41.6% share, driven by extensive defense budgets, robust digital infrastructure, and the early adoption of advanced technologies. In 2025, the regional market is valued at over USD 6.2 billion, supported by key players such as Raytheon Technologies, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman. The U.S. Department of Defense’s emphasis on AI-enabled cyber resilience and its Defend Forward strategy are reshaping national cyber defense capabilities.
Europe holds a significant share, backed by NATO’s collective cybersecurity initiatives and increasing investment from countries like Germany, France, and the UK in digital defense infrastructure. Collaborative frameworks such as the EU’s Permanent Structured Cooperation (PESCO) are also strengthening cross-border cybersecurity capabilities.
Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, with an expected CAGR exceeding 16% through 2034. Heightened geopolitical tensions, especially in the South China Sea and Indo-Pacific regions, have led nations such as China, India, South Korea, and Japan to accelerate defense digitalization programs. These include indigenous cybersecurity frameworks, secure satellite communications, and cyber warfare training units.
Latin America, though currently in a nascent stage, is beginning to invest in cybersecurity for border protection and critical infrastructure. The Middle East & Africa are witnessing growth driven by rising cyber threats targeting energy infrastructure and growing defense modernization efforts in countries like Israel, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMarket Key Segments
By Component
- Software and Services
- Hardware
By Solution Type
- Cyber Threat Protection
- Content Security
- Threat Evaluation
- Other Solution Types
By Application
- Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience
- Cloud Security
- Application Security
- Other Applications
By End-User
- Land Force
- Naval Force
- Air Force
Regions
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 17.3 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 72.4 B |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 17.2% |
| Historical data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | By Component (Software and Services, Hardware), By Solution Type (Cyber Threat Protection, Content Security, Threat Evaluation, Other Solution Types), By Application (Critical Infrastructure Security and Resilience, Cloud Security, Application Security, Other Applications), By End-User (Land Force, Naval Force, Air Force) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Leonardo S.p.A., Accenture plc, Thales Group, The Boeing Company, L3Harris Technologies, Inc., Elbit Systems Ltd., BAE Systems Plc, General Dynamics Mission Systems, Inc., Lockheed Martin Corporation, Northrop Grumman Corporation, Other Key Players |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Defense Cybersecurity Market
Published Date : 18 Nov 2025 | Formats :Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date