Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity Market Size USD 4.05B & 4.8% CAGR
Global Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity Market Size, Share & Clinical Research Analysis By Drug Class, By Diagnostic Method, By Indication (Oncology, Autoimmune, Infectious Diseases), By End User, Regulatory Landscape, R&D Trends & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
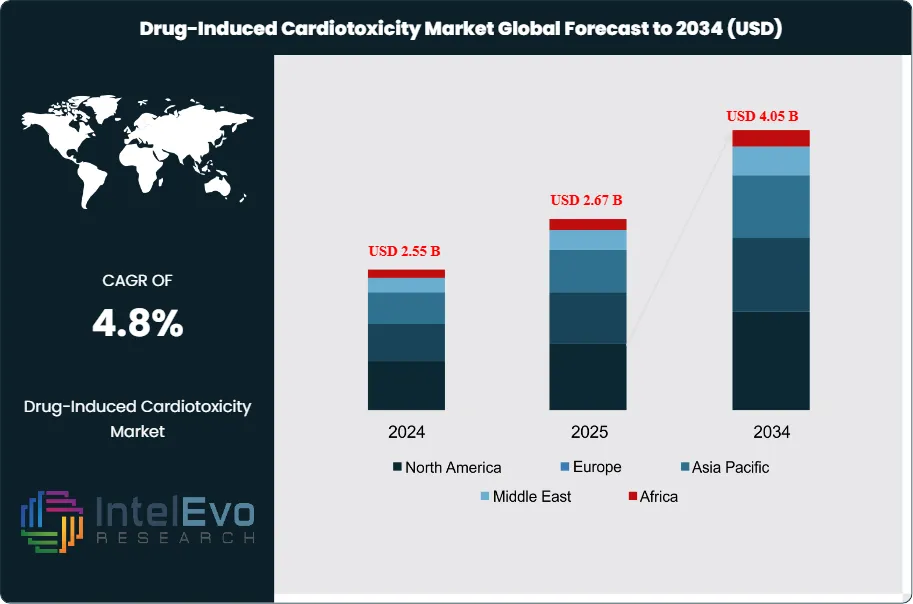
The Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity Market is estimated at USD 2.55 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach approximately USD 4.05 billion by 2034, registering a CAGR of about 4.8% during 2025–2034. Market growth is driven by the rising use of oncology, immunotherapy, and targeted small-molecule drugs with known cardiovascular risk profiles, alongside stricter cardiac safety monitoring requirements in clinical development. Increasing adoption of early-stage cardiotoxicity screening, biomarker-based risk assessment, and advanced imaging is improving patient outcomes and reducing late-stage drug attrition. In parallel, closer collaboration between pharma sponsors, CROs, and cardio-oncology specialists is positioning cardiotoxicity evaluation as a standard component of modern drug development pipelines.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportDemand reflects a larger oncology and specialty-drug pipeline, an aging patient base, and tighter safety expectations across regulators and payers. Historical recalls and label changes tied to QT prolongation, left ventricular dysfunction, and arrhythmias have kept cardiovascular safety at the center of clinical risk. Reported cardiotoxicity rates in breast cancer chemotherapy cohorts range from 6% to 28%. Chemotherapy exposure raises cardiovascular event incidence by about 30%. Cardiac adverse events remain a frequent cause of late-stage attrition and account for a meaningful share of post-market actions.
Growth will track earlier detection, safer regimens, and better risk stratification. You see broader uptake of structured cardiac monitoring in oncology protocols, with routine echocardiography, global longitudinal strain, and biomarker panels such as troponin and NT-proBNP. FDA and EMA require cardiovascular assessments from preclinical through Phase III under ICH E14 and S7B guidance; sponsors face higher evidence bars for HER2 therapies, anthracyclines, TKIs, and some antidepressants. Risks remain. Multi-drug regimens amplify exposure. Real-world polypharmacy can unmask QT liabilities. Cost and workflow burden constrain universal surveillance in lower-resource settings. Still, clinical practice is moving to standardized cardio-oncology pathways that link oncology, cardiology, and pharmacovigilance teams.
Technology is reshaping screening and prediction. iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, organ-on-chip models, and automated patch-clamp platforms shift detection earlier and reduce false negatives. High-content imaging and machine learning models improve hazard classification from in vitro signals to in vivo risk. AI-enabled ECG analytics and predictive algorithms flag at-risk patients before symptomatic decline. Digital endpoints and remote monitoring shorten feedback loops between dose changes and cardiac response. These tools cut late failures and support safer label claims when paired with prospective validation.
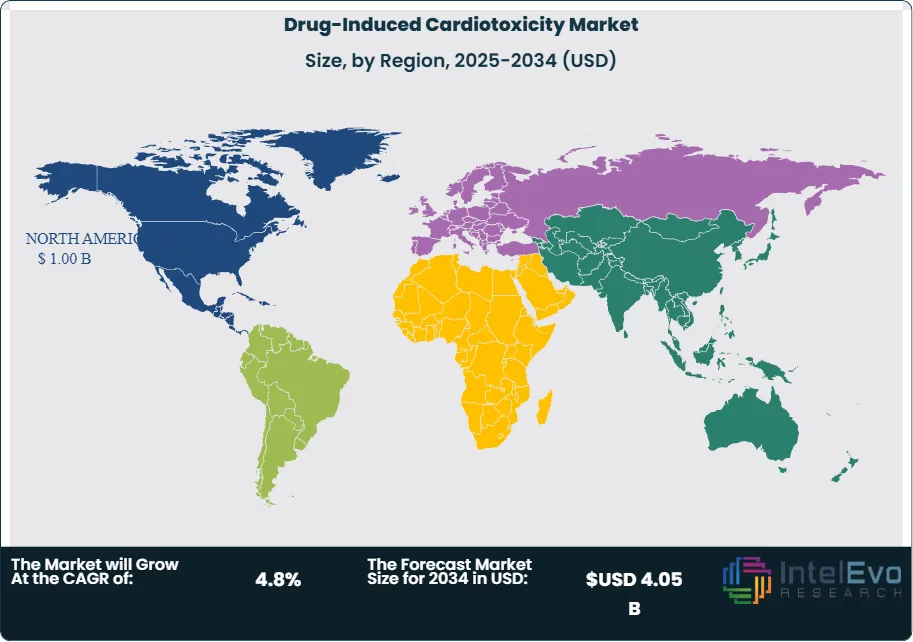
Regionally, North America leads on funding, trial density, and cardio-oncology networks. The NIH committed sizable grants to biomarker discovery and AI methods, reinforcing the U.S. evidence base. Europe benefits from EMA guidance, strong registries, and Horizon-backed consortia focused on safety pharmacology. Asia Pacific is the fastest growing on the back of rising oncology incidence, expanding biopharma R&D in China and Japan, and investment in contract research infrastructure. Investors should watch U.S. and EU hubs for platform advances, while Asia offers scale in trials and manufacturing for translational tools and monitoring solutions.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The market stands at USD 2.55 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 4.05 billion by 2034 at a 4.8% CAGR, supported by rising oncology exposure and structured safety monitoring in trials and care pathways. Chemotherapy cohorts report cardiotoxicity rates of 6–28%, with roughly a 30% increase in cardiovascular events, sustaining demand for earlier detection and risk management.
- Type: Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity leads with over 67% share in 2023, driven by broad use of anthracyclines and targeted agents that require intensive surveillance and mitigation protocols. This concentration keeps sponsors and providers focused on cardio-oncology workflows and post-market vigilance.
- Detection: Biomarkers hold 53% of the detection segment as of 2023, reflecting their integration into routine monitoring and trial endpoints for earlier signal capture. Biomarker-linked solutions also account for 39% within drug class analytics, reinforcing their role in decision-making and labeling support.
- Driver: Expanding cancer therapy utilization and documented cardiotoxicity prevalence are lifting screening and monitoring adoption across care settings. Biomarker-centric workflows scale fastest, anchored by majority share in detection and growing incorporation into real-world protocols.
- Restraint: Adoption is uneven across regions, with North America holding 39.4% share and USD 0.55 billion in 2023, signaling access and budget constraints in emerging markets. The modest global trajectory of 4.6% CAGR underscores cost sensitivity and workflow burden for universal surveillance.
- Opportunity: AI-enabled cardiotoxicity screening is expanding, with the broader screening market projected to rise from USD 3.17 billion in 2025 to about USD 8.46 billion by 2034 at 11.54% CAGR, creating pull-through for predictive tools and integrated biomarker platforms. You can align portfolios to AI-assisted ECG analytics, image-based phenotyping, and risk scoring to capture faster-growing budgets adjacent to core monitoring.
- Trend: The market is shifting toward biomarker-first detection and AI augmentation across research and clinical workflows, consolidating share in laboratory and software-driven solutions. AI adoption in screening is accelerating, with long-run double-digit growth reinforcing demand for predictive models that reduce late-stage attrition and adverse event burden.
- Regional Analysis: North America leads at 39.4% share with USD 0.55 billion, supported by concentrated trial activity and established cardio-oncology networks. Across the 7 major markets, cardiotoxicity-related spending is projected to grow at about 4.37% CAGR through 2035, indicating steady but disciplined investment profiles in mature regions.
Type Analysis
Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity remains the largest segment. It accounted for more than 67% of market revenue in 2023 and will hold leadership through 2030 as oncology regimens expand and survivorship rises. Anthracyclines, trastuzumab, and select TKIs drive most monitoring demand, prompting routine baselines, serial echocardiography, and biomarker panels in cancer centers. You should plan for sustained protocol adoption as health systems link oncology and cardiology teams to cut dose-limiting cardiac events.
Antipsychotic drug-induced cardiotoxicity is smaller but growing. Long-term exposure to antipsychotics with QT prolongation risks, combined with rising mental health prevalence, supports steady uptake of ECG and QTc surveillance. Expect mid-single-digit growth as payers formalize baseline and follow-up testing in high-risk patients and as hospitals embed risk scores into prescribing pathways.
Detection Analysis
Biomarkers lead detection with more than 53% share. High-sensitivity troponin and NT-proBNP have become the default early-warning tools in trials and routine care due to low incremental cost and rapid turnaround. Adoption accelerates when paired with order sets and reflex testing; you can expect 6–7% annual growth as labs integrate automated reporting and clinicians lean on serial delta thresholds for decision-making.
Imaging techniques are essential for confirmation and quantification. Global longitudinal strain echocardiography improves early detection of subclinical dysfunction, while cardiac MRI with T1/T2 mapping clarifies edema and fibrosis. Health systems increasingly combine biomarkers with strain or MRI to reduce false negatives and guide therapy adjustments. Machine learning tools that assist ECG and image interpretation are entering practice, improving triage and throughput in cardio-oncology clinics.
Drug Class Analysis
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors are the most consequential drug class for monitoring demand. Class effects include hypertension, QT prolongation, and left ventricular dysfunction, which trigger protocolized surveillance across HER2, BTK, VEGF, and ALK portfolios. As TKI indications expand, you will see higher test volumes per patient and earlier intervention thresholds to maintain dose intensity.
Antibiotics and NSAIDs add measurable risk in polypharmacy. Macrolides and fluoroquinolones carry QT concerns, while NSAIDs elevate heart failure and ischemic risks in susceptible patients. Hospitals respond with stewardship, ECG gating for high-risk antibiotics, and biomarker-first pathways in acute care. Biomarkers represent about 39% within drug-class analytics, reinforcing their role in triage and longitudinal monitoring.
Regional Analysis
North America leads with roughly 39.4% share and about USD 0.55 billion in 2023, supported by strong trial density, NIH-backed research, and mature cardio-oncology networks. Reimbursement for echocardiography, strain analysis, and key biomarkers sustains high utilization across academic and integrated delivery systems. Vendors gain from clear clinical guidelines and robust data infrastructure.
Europe ranks second on the strength of EMA guidance, national registries, and Horizon-funded consortia focused on safety pharmacology. Adoption is broad in Western Europe, with Central and Eastern Europe catching up as budgets improve. Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region as oncology incidence rises and R&D scales in China and Japan; expect high single-digit growth as leading centers standardize biomarker–imaging protocols. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are emerging with private hospital investment and selective payer coverage, though budgets and capacity remain the main constraints.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMarket Segment
Type Analysis
- Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- Antipsychotic Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Detection Analysis
- Biomarker-Based Detection
- Imaging-Based Detection
Drug Class Analysis
- Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs)
- Antibiotics and NSAIDs
Regional Analysis
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 2.55 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 4.05 B |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 4.8% |
| Historical data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | Type Analysis (Chemotherapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity, Antipsychotic Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity), Detection Analysis (Biomarker-Based Detection, Imaging-Based Detection), Drug Class Analysis (Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs), Antibiotics and NSAIDs) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Roche Diagnostics, Abbott Laboratories, Siemens Healthineers, QuidelOrtho, GE HealthCare, Philips Healthcare, Canon Medical Systems, Bruker, IQVIA, Labcorp Drug Development, Charles River Laboratories, ICON plc, Ultromics, Caption Health |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Drug-Induced Cardiotoxicity Market
Published Date : 24 Dec 2025 | Formats :Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date