eVTOL Aircraft Market Size, Growth, Trends & Forecast 2025–2034
Global eVTOL Aircraft Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis by Aircraft Type (Passenger eVTOL, Cargo eVTOL, Air Taxi), by Propulsion & Power Source (Battery Electric, Hybrid Electric), by Range & Payload Capacity, by Application (Urban Air Mobility, Air Taxi Services, Logistics & Cargo, Emergency Medical Services, Defense & Security), by End User (Commercial Operators, Government & Defense), Regional Outlook, Key Players, Market Dynamics, Investment Trends & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
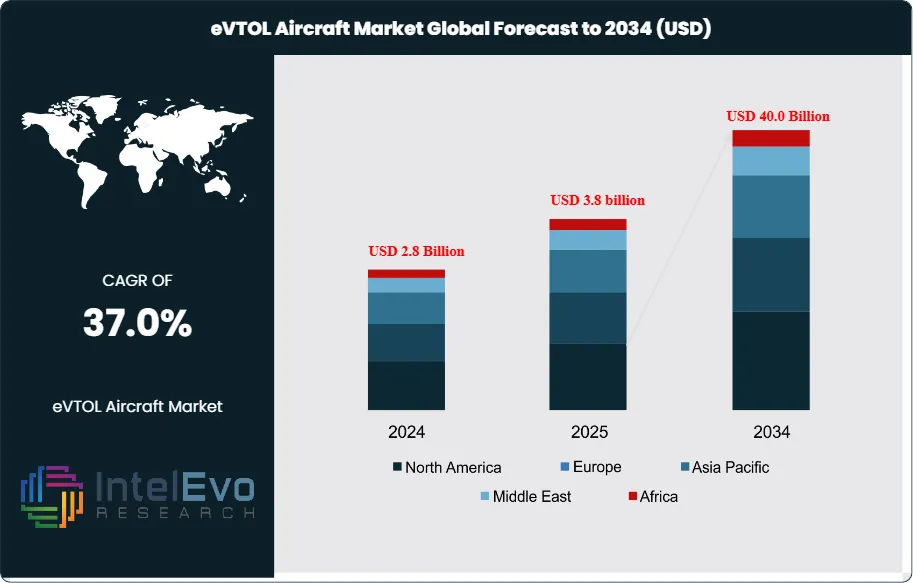
The eVTOL Aircraft Market is estimated at USD 2.8 billion in 2024 and is on track to reach roughly USD 40 billion by 2034, implying a compound annual growth rate of 37.0% over 2025–2034. This exceptional growth trajectory is driven by accelerating investments in urban air mobility, rising demand for sustainable aviation solutions, and strong backing from governments and private investors. Rapid advancements in battery technology, autonomous flight systems, and regulatory frameworks are further bringing commercial eVTOL deployment closer to reality. As major aerospace players and startups race toward certification and pilot programs, the market is positioned to redefine short-distance air transport over the next decade.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportThis projection reflects rapid commercialisation driven by improvements in battery energy density, falling unit costs, and sustained private and public capital inflows. Base-year revenues concentrate in demonstrator programs and early commercial pilots, while 2034 revenues shift to recurring operations and service contracts. By 2034, commercial intra-city travel and air taxi services are projected to represent roughly 45% of total market revenue, emergency medical services 20%, and cargo and logistics 15%, with the balance from training, maintenance, and infrastructure fees.
Demand dynamics show strong urban adoption where average trip distances are under 100 miles and congestion imposes high economic costs. Supply-side forces include OEM scale-up, battery cell capacity expansion, and new vertiport construction. Battery energy density gains average 6–8% per annum in industry forecasts. Integration of AI and automation reduces pilot-related operating expense by an estimated 15–25% and improves dispatch efficiency. Digitalisation of traffic management and predictive maintenance will lift aircraft utilisation by an estimated 10 percentage points relative to current rotorcraft norms.
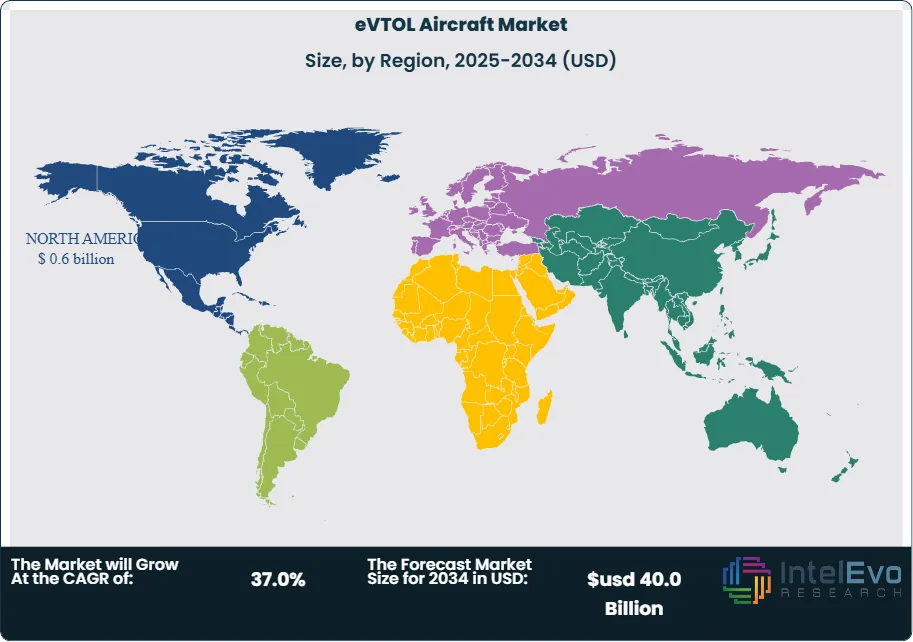
Regulatory frameworks present a mixed picture. Certification timelines shorten in jurisdictions with clear UAM roadmaps, while airspace integration and noise ordinances extend project lead times in dense urban centres. Noise levels near 65 decibels support closer urban operations compared with helicopters. Governments in North America and Asia Pacific have announced funding and trials that position those regions as investment hotspots. Market share by region for 2024 is estimated at North America 40%, Asia Pacific 30%, Europe 20%, Rest of World 10%. By 2034, Asia Pacific share rises to 35% as domestic mobility programs scale.
Key risk factors include battery raw material supply constraints, certification delays, public acceptance following any safety incident, and infrastructure permitting. Financing risk concentrates in late-stage manufacturing funding where capital intensity escalates. Strategic opportunities exist in vertically integrated service models and in software-enabled fleet management. Investors should treat timelines as contingent on regulatory progress and onshore industrial policy. Operational metrics, including a typical range of 60–100 miles and per-flight emission reductions up to 80% relative to conventional aviation, support a strong case for continued capital deployment.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The global eVTOL aircraft market grows from USD 2.8 billion in 2024 to USD 40.0 billion by 2034. The CAGR reaches 36.8 percent, driven by higher investment in urban air mobility programs and steady improvements in battery performance.
- Lift Technology: Vectored Thrust leads the lift technology segment with 42.1 percent share in 2024. OEMs favor this configuration for higher control authority and better payload efficiency during commercial operations.
- Mode of Operation: Piloted aircraft hold a 33.2 percent share in 2024. Regulators and operators rely on piloted models to speed up certification and early route approvals while autonomous systems mature.
- Range: The 200–500 km range category accounts for 56.7 percent of the market in 2024. Operators prefer this range for high-frequency regional and urban missions that balance payload, energy use, and route profitability.
- Maximum Take-off Weight: Units under 250 kg secure 28.5 percent share in 2024. These models attract interest from cargo and short-hop service providers due to lower development costs and simplified regulatory requirements.
- Application: Commercial use cases lead with 47.5 percent share in 2024. Demand rises for scheduled air taxi operations, regional connectors, and medical transport services in congested metro areas.
- Driver: Battery density increases by roughly 6 to 8 percent each year, enabling longer routes and lower operating cost. OEMs report double-digit reductions in energy expense as pack efficiency improves.
- Restraint: Certification timelines extend project launch dates by 12 to 24 months in several markets. Airspace integration and noise rules slow scale-up for operators planning dense urban routes.
- Opportunity: Asia Pacific emerges as a high-growth region. National mobility programs support double-digit fleet expansion and signal strong demand for aircraft in the 200–500 km category.
- Trend: Automation and AI-based flight management reduce pilot workload and strengthen safety systems. Early testing shows up to 20 percent improvement in dispatch reliability for fleets using advanced analytics.
- Regional Analysis: North America holds 36.5 percent share and USD 0.62 billion revenue in 2024. Asia Pacific gains momentum at a faster CAGR due to infrastructure investment and early commercial trials.
Lift Technology Analysis
The lift technology landscape continues to shift as the eVTOL market enters 2025 with growing commercial trials and certification activity. Vectored Thrust retains the largest position, holding more than 42 percent of global deployments in the latest assessment. Operators value this configuration for its maneuverability during dense urban operations and for its ability to support higher-speed routes. Multirotor platforms maintain close to 30 percent share. You see this segment gain steady interest from service providers targeting short-range, high-frequency missions where simplicity and redundancy remain priorities.
Lift Plus Cruise follows with roughly 28 percent share. This hybrid configuration appeals to programs focused on extended-range regional links. The segment benefits from advances in battery output and lighter propulsion assemblies, which extend effective range while controlling noise levels. Certification bodies across North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific continue to test performance and safety standards for all three architectures. The rising pipeline of commercial air taxi pilots signals stronger adoption across these lift categories through 2030.
These lift technologies shape investment decisions for aircraft developers and infrastructure partners. Each configuration presents different performance limits, cost structures, and regulatory pathways. Your assessment of route planning, battery cycles, and maintenance profiles will determine which models deliver the strongest returns in early commercial networks.
Mode of Operation Analysis
Piloted aircraft lead the operational mix heading into 2025 with more than 33 percent share. Regulators continue to prioritize piloted systems for initial passenger services, which supports faster approval cycles and stronger public confidence. Semi-autonomous configurations follow closely with a similar share. Operators adopt these systems to reduce cockpit workload and improve routing accuracy during high-density operations.
Autonomous aircraft hold close to 34 percent share. Their growth accelerates as AI-based flight management, detect-and-avoid sensors, and cloud-based traffic coordination improve. You see major OEMs preparing for phased transitions from piloted to fully autonomous operations as infrastructure and regulatory frameworks mature. Testing corridors in the United States, Europe, China, and the Gulf states show rising flight hours, which helps validate autonomy software and maintenance standards.
This mix reflects an industry balancing safety requirements with the cost benefits of automation. As regulators publish new frameworks for autonomous passenger and cargo missions, adoption rates across semi-autonomous and autonomous systems will rise through the next decade.
Range Analysis
The 200 to 500 km range class holds more than 56 percent share in the latest dataset. This segment fits emerging air taxi and regional mobility routes where operators seek to replace short-haul ground transport. Aircraft in this category benefit from steady gains in lithium-based battery density and thermal management. The 0 to 200 km segment continues to serve inner-city applications. It attracts interest from delivery networks and medical response providers who value rapid turnaround times and smaller landing footprints.
Route economics drive these share distributions. Longer-range models deliver higher revenue per trip and support intercity operations, while shorter-range aircraft fit dense mobility networks in metro regions. Battery costs and charging infrastructure expansion will influence segment growth through 2030.
Maximum Take-off Weight Analysis
Aircraft under 250 kg secured more than 28 percent share in the most recent analysis. This category expands in logistics and emergency support due to lower certification hurdles and lower operating expenses. Programs above 1500 kg form the fastest-growing category, supported by commercial passenger operators and defense agencies seeking higher payload capacity and extended mission ranges.
Weight class selection shapes procurement strategies. Lighter aircraft provide faster deployment cycles, while higher-weight platforms deliver broader mission versatility. Your operational model determines which category offers the strongest margins.
Propulsion Type Analysis
Battery-electric systems remain the dominant propulsion type in 2025 deployments. Their share rises as energy density improves and charging infrastructure expands across major cities. Hybrid-electric aircraft gain interest for regional missions where operators need higher reliability during extended flights. Hydrogen-electric propulsion remains in early testing. Japan, Germany, and the United States report progress in fuel-cell integration, positioning the segment for gradual adoption after 2030.
Propulsion choices influence cost per flight, emission reductions, and maintenance scheduling. Operators planning long-range services may consider hybrid systems, while urban operators benefit from the lower operating cost of battery-electric aircraft
Application Analysis
Commercial services account for more than 47 percent of global eVTOL demand. Air taxi programs, scheduled regional links, and express logistics drive this segment. Military agencies increase investment in surveillance, perimeter security, and rapid-response missions. Emergency medical services emerge as a high-growth segment. Faster response times and lower operating cost attract interest from hospitals and public agencies evaluating alternatives to traditional rotorcraft.
Each application category carries its own regulatory and certification requirements. You will see adoption accelerate as authorities approve dedicated air corridors for passenger and cargo flights.
By End-Use
Commercial buildings represent the highest adoption rate as property developers integrate vertiports into mixed-use projects. Real estate groups in the United States, UAE, and South Korea announce partnerships to enable rooftop access for air taxi operations. Residential demand grows in premium developments that plan private landing pads. Industrial facilities evaluate eVTOLs for site-to-site transport and emergency operations.
End-use patterns align with urban congestion levels, land availability, and local permitting rules. Markets with strong public-private partnerships move faster toward integration.
Regional Analysis
North America leads with more than 36 percent share and revenue above USD 0.6 billion. The region benefits from strong OEM presence, FAA-led regulatory pathways, and early vertiport development in major cities. Europe follows with steady progress supported by environmental mandates and joint government-industry pilot programs.
Asia Pacific records the fastest growth. China, South Korea, and Japan increase flight testing and invest in hydrogen and battery-electric propulsion ecosystems. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa remain early-stage markets. Both regions explore eVTOL corridors for tourism, medical response, and remote-area access.
Regional adoption will depend on airspace regulation, infrastructure funding, and public readiness for aerial mobility services through 2035.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMarket Key Segments
By Lift Technology
- Vectored Thrust
- Multirotor
- Lift Plus Cruise
By Mode of Operation
- Piloted
- Autonomous
- Semi-Autonomous
By Range
- 0-200 Km
- 200-500 Km
By Maximum Take-off Weight (MTOW)
- <250 Kg
- 250-500 Kg
- 500-1500 Kg
- >1500 Kg
By Propulsion Type
- Battery-Electric
- Hybrid-Electric
- Hydrogen-Electric
By Application
- Commercial
- Military
- Emergency Medical Service
Regions
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 2.8 Billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | usd 40.0 Billion |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 37.0% |
| Historical data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | By Lift Technology, Vectored Thrust, Multirotor, Lift Plus Cruise, By Mode of Operation, Piloted, Autonomous, Semi-Autonomous, By Range, 0-200 Km, 200-500 Km, By Maximum Take-off Weight (MTOW), <250 Kg, 250-500 Kg, 500-1500 Kg, >1500 Kg, By Propulsion Type, Battery-Electric, Hybrid-Electric, Hydrogen-Electric, By Application, Commercial, Military, Emergency Medical Service |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | EHang Holdings Ltd., Beta Technologies, Elbit Systems Ltd., Joby Aviation, Volocopter, Airbus SE, Jaunt Air Mobility, EHang Holdings Limited |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date