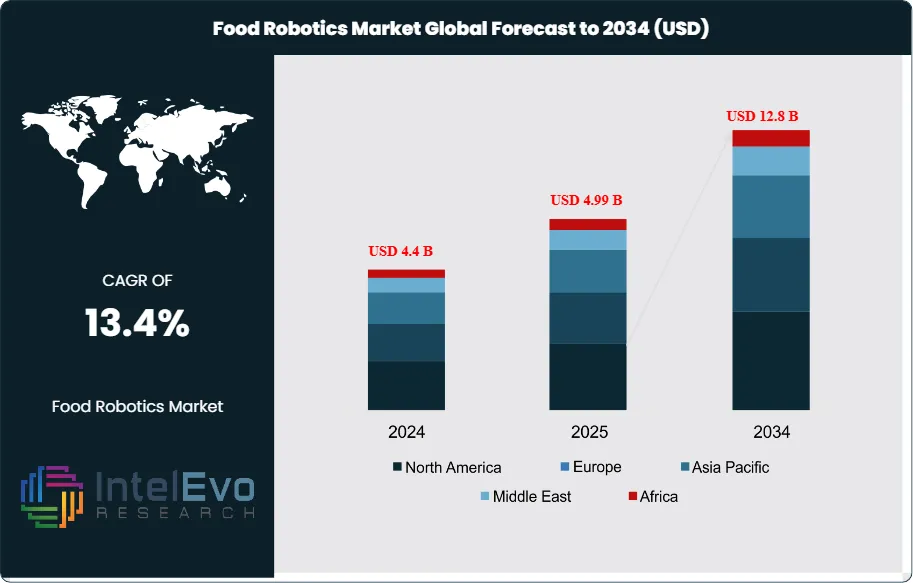
The Food Robotics Market is valued at USD 4.4B in 2024 and will reach USD 12.8B by 2034, growing at a 13.4% CAGR. Discover key trends driving automation in food processing.
Global Food Robotics Market Size, Share & Analysis Type (Articulated Robots, Collaborative Robots, Parallel Robots, Cylindrical Robots, Cartesian Robots, SCARA Robots), Payload Capacity (Low Payload Robots, Medium Payload Robots, High Payload Robots), Application (Packaging and Repackaging, Palletizing, Processing, Pick and Place), By End-User (Bakery, Dairy, Meat & Poultry, Beverage) Industry Regions & Key Players – Automation Drivers, Labor Cost Impact, Technology Roadmap & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
The Food Robotics Market is valued at USD 4.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach approximately USD 12.8 billion by 2034, reflecting a strong CAGR of about 13.4% during 2025–2034. This rapid growth shows how automation is becoming a core pillar for modern food processing, safety, and packaging operations. Rising labor shortages, higher hygiene standards, and the push for precision-driven production continue to accelerate robotic adoption globally. With AI-enabled robotics, collaborative robots (cobots), and high-speed pick-and-place systems transforming the food value chain, the market is quickly gaining attention across social and professional platforms.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMomentum reflects a structural shift toward automated processing, packing, and quality control as producers seek higher throughput, hygienic operations, and resilience against chronic labor gaps. After steady single-digit gains pre-2020, adoption has broadened across proteins, bakery and confectionery, ready-to-eat meals, and fresh-produce handling. The sector benefits from the wider industrial automation backdrop—an installed base of ~3 million industrial robots globally and ~400,000 incremental units shipped each year—alongside a reported ~88% of manufacturers planning deeper robotics integration over the medium term.
Demand-side catalysts are clear: food safety regimes (e.g., FSMA in the U.S., EU hygiene packages) and retailer audit standards are pushing washdown (often IP69K) designs, traceable workflows, and automated clean-in-place. Plants implementing vision-guided pick-and-place and end-of-line cells typically report 15–30% higher line throughput and 10–15% lower scrap, while 3D vision and force-torque control can add 1–2 percentage points of recoverable yield in deboning. At the same time, SKU proliferation and shorter runs elevate the need for flexible changeovers and modular cells. Key constraints persist—high upfront capex, integration with legacy PLC/MES systems, sanitation validation, and a shortage of robotics technicians—keeping payback periods in the 18–30-month range for many SME deployments and emphasizing the importance of service partnerships and cybersecurity hardening.
Technology is evolving quickly: AI/ML perception, soft-gripping, and digital twins are moving robots “upstream” into delicate primary handling of produce and bakery items, while collaborative robots (cobots) are expanding in brownfield lines due to small footprints and safe human-robot interaction. Pre-engineered cells, simulation-driven commissioning, and Robotics-as-a-Service models are compressing time-to-value and reducing capital intensity, opening the door for mid-market processors. Data infrastructure—edge analytics, vision libraries, and connectors to MES/ERP/LIMS—is becoming a differentiator as manufacturers target predictive maintenance and real-time quality release.
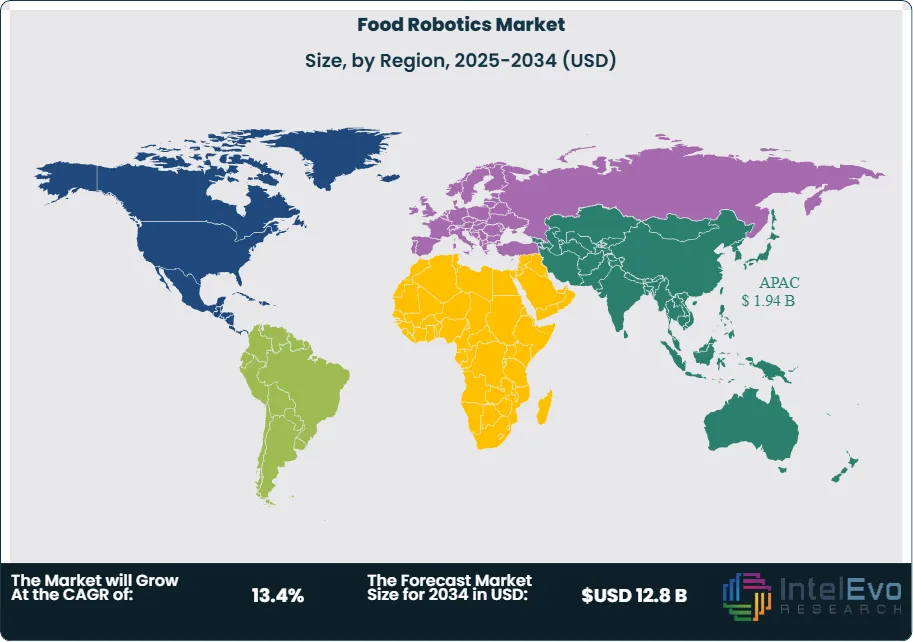
Regionally, Asia–Pacific accounts for the largest share (approximately 40–45%) on the strength of China, Japan, and South Korea’s OEM ecosystems and smart-factory policies; North America is an investment hotspot with low-teens CAGR driven by protein processing upgrades and compliance mandates; and Western Europe (circa 28–30% share) leverages a dense machine-builder network and sustainability-oriented packaging. Investors should also watch India, Southeast Asia, the Gulf, and Brazil, where cold-chain buildouts and modern retail are accelerating end-of-line automation.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The global Food Robotics market was USD 4.4 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 12. 8 billion by 2034 (13.4% CAGR), propelled by hygiene-driven automation, persistent labor shortages, and AI-enabled quality assurance that lifts line throughput by 15–30% and trims scrap by 10–15%.
- Robot Type: Articulated robots lead with ~50% revenue share (2024e) due to payload flexibility for cutting, portioning, and palletizing; SCARA/delta platforms are the fastest-growing (≈12–14% CAGR) on high-speed pick-and-place and secondary packaging.
- Application: Packaging & palletizing account for ~42% of revenues, supported by SKU proliferation and retailer compliance needs; primary processing (meat, poultry, and seafood) is accelerating as soft-grip end effectors and washdown IP69K designs expand robots into raw handling.
- Driver: Tightening food safety regimes (e.g., FSMA in the U.S. and EU hygiene directives) are shifting specifications toward sanitary designs, automated clean-in-place, and traceability—boosting adoption in new lines where automation is now embedded in >70% of greenfield projects at tier-one processors.
- Restraint: High upfront and integration costs—typically USD 250k–800k for a vision-guided, washdown-rated cell—extend payback for SMEs to 24–36 months; validation for sanitation and changeovers can add weeks to commissioning, increasing total project risk.
- Opportunity: Cobots and Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) in mid-sized plants represent the fastest-growing commercialization model (≈15%+ CAGR), lowering capex and enabling rapid deployment in bakery, confectionery, and ready-meal assembly where cycle times and payloads fit collaborative envelopes.
- Trend: Convergence of AI/ML vision, 3D perception, and tactile/soft-gripping is unlocking delicate produce and bakery handling; major vendors (ABB, FANUC, Yaskawa, KUKA, Stäubli) and emerging players are launching pre-engineered cells with digital twins that cut integration time by 20–30%.
- Regional Analysis: Asia–Pacific leads with ~40–45% revenue share on dense OEM ecosystems and rapid line modernization in China, Japan, and South Korea; North America is the growth hotspot (≈12% CAGR) driven by compliance and protein processing investments, while Western Europe (~28–30% share) scales upgrades in packaging and intralogistics amid strong machine-builder networks.
Type Analysis
Articulated robots remain the backbone of food automation, accounting for roughly 35% of global revenues in 2023 and expected to maintain ~38–40% share through 2030 as processors standardize on hygienic, IP69K-rated arms for cutting, portioning, depanning, and end-of-line tasks. Their ability to pair multi-axis motion with AI/3D vision and soft-gripping has widened the feasible use-case set from raw protein handling to precision cake decoration, lifting line throughput by 15–25% while stabilizing yields. SCARA and parallel (delta) platforms are the high-speed workhorses for primary packaging and top-loading, together representing ~25–28% of deployments; continued miniaturization and tool-less changeovers position these systems for double-digit growth in snack, bakery, and confectionery lines.
Collaborative robots (cobots) are the fastest-growing type (≈14–16% CAGR, 2025–2030), winning in brownfield upgrades where footprint, ease of programming, and safe human–robot interaction are decisive. Cylindrical and Cartesian robots, while niche, retain relevance in cost-sensitive, repetitive motions such as tray loading and icing, particularly for SMEs; collectively they are expected to sustain mid-single-digit growth as vendors bundle pre-engineered cells and digital twins that cut integration effort by 20–30%.
Application Analysis
Packaging and repackaging is the largest application, representing an estimated 40–42% of 2025 spending as retailers enforce tighter case-ready standards and SKU proliferation drives demand for flexible, quick-change automation. Vision-guided inspection embedded at this stage typically trims scrap by 10–15% and reduces customer returns, reinforcing the business case. Palletizing remains the number-two use case (~25–27% share), with high-payload arms and layer-forming gantries eliminating end-of-line bottlenecks; modern cells achieve >95% uptime and 15–30% higher hourly throughput versus manual stations.
Processing and pick-and-place are scaling rapidly as soft robotics, force–torque sensing, and food-safe end effectors enable delicate manipulation of baked goods, produce, and raw protein. Adoption in these mid-line tasks is forecast to outpace the overall market (≈12–14% CAGR) as plants target hygiene, labor stability, and traceability gains within Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) regimes.
End-User Analysis
Beverage companies lead adoption (~23% share in 2023; high single-digit growth through 2030) given high speed bottling, capping, and case packing needs; multi-format changeovers and RaaS offerings are expanding penetration among regional bottlers. Bakery and confectionery producers are close behind, leveraging delta/SCARA systems for gentle handling and secondary packaging; sites typically report 20%+ cycle-time improvements and rapid paybacks (18–24 months).
Meat, poultry, and seafood processors are a structural growth engine (≈12–14% CAGR) as washdown-rated arms and 3D vision stabilize yields in deboning and trimming, often adding 1–2 percentage points of recoverable product margin. Dairy, and fruits & vegetables processors are scaling cobots and soft-grip solutions to reduce contamination risk and bruising, respectively; predictive maintenance integrated with MES is cutting unplanned downtime by 10–20% across early adopters.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific is the demand epicenter, having captured ~43% of revenues in 2023 and on track to approach 45% by 2030. China, Japan, and South Korea anchor installed base growth with robust machine-builder ecosystems and policy support for “smart factories,” while India and Southeast Asia are emerging as fast followers as cold-chain capacity expands.
North America is an investment hotspot (≈11–13% CAGR, 2025–2030), propelled by persistent labor tightness, FSMA-aligned food safety requirements, and modernization in protein processing. Europe maintains a substantial share (~28–30%) underpinned by strong OEM networks in Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands and a pivot to sustainable packaging automation. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa remain smaller but accelerating (≈9–11% and 8–10% CAGRs, respectively) as multinational food groups localize production, with Brazil, Mexico, the UAE, and Saudi Arabia prioritizing high-throughput packaging and palletizing cells to support retail consolidation and export growth.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportKey Market Segments
Type
- Articulated Robots
- Collaborative Robots
- Parallel Robots
- Cylindrical Robots
- Cartesian Robots
- SCARA Robots
- Other Types
Payload Capacity
- Low Payload Robots
- Medium Payload Robots
- High Payload Robots
Application
- Packaging and Repackaging
- Palletizing
- Processing
- Pick and Place
- Other Applications
End-User
- Beverages Companies
- Dairy Companies
- Bakery and Confectionery Companies
- Meat, Poultry, and Seafood Companies
- Fruits and Vegetables Companies
- Other End-Users
Regions
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 4.4 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 12.8 B |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 13.4% |
| Historical data | 2018-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | Type (Articulated Robots, Collaborative Robots, Parallel Robots, Cylindrical Robots, Cartesian Robots, SCARA Robots, Other Types), Payload Capacity (Low Payload Robots, Medium Payload Robots, High Payload Robots), Application (Packaging and Repackaging, Palletizing, Processing, Pick and Place, Other Applications), End-User (Beverages Companies, Dairy Companies, Bakery and Confectionery Companies, Meat, Poultry, and Seafood Companies, Fruits and Vegetables Companies, Other End-Users) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Stäubli International AG, FANUC CORPORATION, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, ABB Group, Seiko Epson Corporation, Yaskawa Electric Corporation, KUKA AG, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd., OMRON Corporation, Universal Robots A/S, Other Key Players |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date