Marine Composites Market Size, Share & Growth Analysis | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific
Global Marine Composites Market Size, Share, and Industry Analysis by Fiber Type (Glass Fiber, Carbon Fiber, Aramid Fiber), by Resin Type (Polyester, Vinyl Ester, Epoxy, Others), by Application (Hull, Deck, Superstructure, Interior Components), by End User (Recreational Boats, Commercial Marine, Naval & Defense, Offshore Wind & Energy) with Regional Insights, Competitive Landscape, Technology Advancements, Sustainability Trends, Market Dynamics, and Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
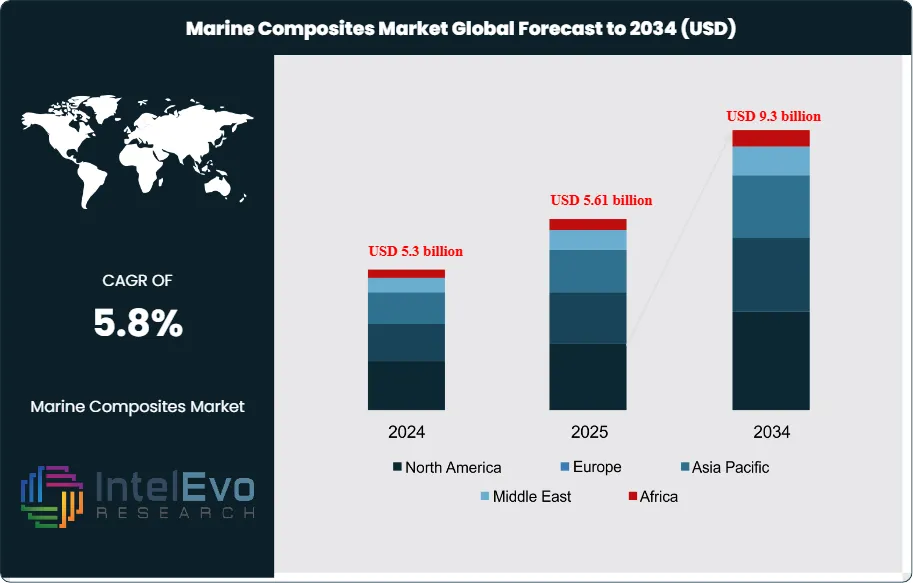
The Marine Composites Market is estimated at USD 5.3 billion in 2024 and is on track to reach roughly USD 9.3 billion by 2034, implying a compound annual growth rate of 5.8% over 2025–2034. This growth is driven by the increasing adoption of lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials in boat hulls, decks, and superstructures to improve fuel efficiency and durability. Rising demand from recreational boating, offshore wind support vessels, and naval modernization programs is further strengthening market momentum. In addition, advancements in fiber-reinforced polymers and resin technologies are enabling longer service life and lower maintenance costs, making marine composites a preferred choice across commercial and defense marine applications.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMarket expansion stems from stronger demand for lightweight, corrosion-resistant, high-strength materials across commercial, defense, and recreational fleets. Shipyards increase composite adoption in hulls, decks, and superstructures as operators pursue fuel savings and higher speed profiles. Changing fleet renewal cycles reinforce this trend, with composite-intensive vessels posting fuel savings near 12% and weight reductions near 25% compared with steel-based builds. These performance gains support a steady shift in procurement strategies across large yards in Europe, North America, and East Asia.
Supply conditions remain stable, supported by consistent output in glass fiber, carbon fiber, and resin systems. Glass fiber holds near 55% share due to competitive pricing and broad application, while carbon fiber advances as producers scale output. Resin innovation shapes supplier competition, with vinyl ester and epoxy systems expected to capture stronger margins through improved thermal resistance and lower maintenance costs. Producers accelerate automation in lay-up processes to limit labor shortages and increase throughput. Digital quality checks and AI-supported defect detection reduce scrap rates and strengthen reliability metrics across high-volume parts.
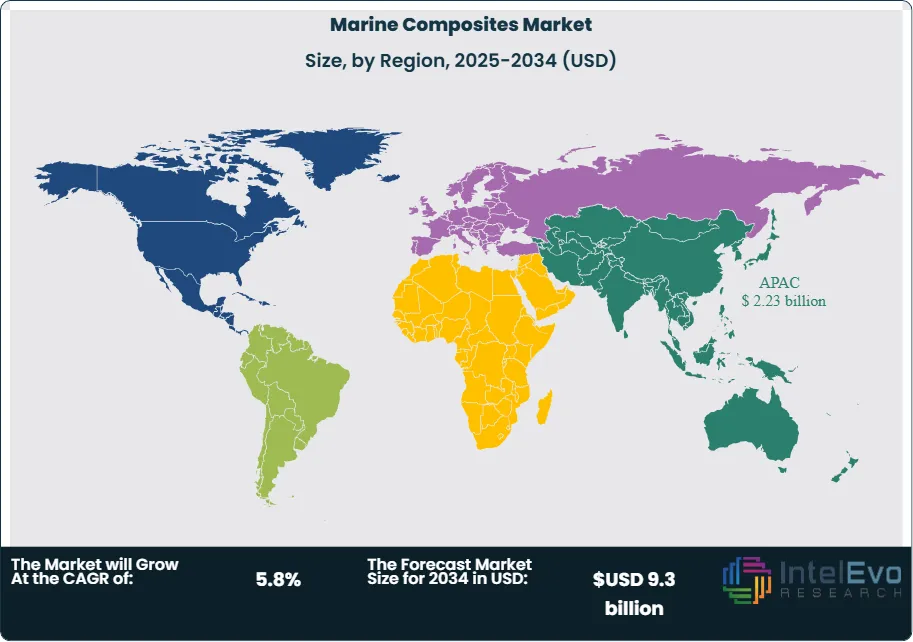
Regulatory actions influence vessel designs across all major regions. Emissions rules under IMO frameworks push builders toward lighter structures. Noise and vibration standards raise demand for composite components with stronger damping properties. Trade rules and import duties add cost pressure in some markets, which encourages investment in regionalized supply chains. North America posts steady growth near 6% per year as coastal enforcement fleets and recreational segments expand. Asia Pacific remains the strongest investment hotspot, capturing near 42% of global demand by 2034, driven by rising leisure craft production in China and South Korea and continued naval procurement in India.
Risk profiles include resin price swings, energy-intensive production stages, and certification challenges for large composite structures. Even with these constraints, composite penetration rises across high-speed craft, ferries, and specialty vessels. Strategic investments in automated molding, digital simulation for structural validation, and integrated recycling systems position leading suppliers to secure long-term share as global fleet needs shift toward lighter and more efficient architectures.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The marine composites market reaches USD 5.3 billion in 2024 and moves toward USD 9.3 billion by 2034. The market posts a CAGR of 5.8 percent as builders shift toward lighter and corrosion-resistant structures.
- Composite Type: Polymer Matrix Composites hold 38.1 percent share in 2023. Their strength, durability, and resistance to harsh marine conditions sustain their lead across hulls, decks, and superstructures.
- Resin Type: Epoxy resin accounts for 36.5 percent share. Its strong adhesion and structural reliability make it the preferred option for high-load areas across performance boats and commercial vessels.
- Vessel Type: Cruise ships use the largest volume of marine composites at 34.5 percent share. Shipyards adopt composite panels and structural parts to limit vessel weight and support fuel savings across large fleets.
- Driver: Demand for high-speed boats, yachts, and performance craft rises across major coastal regions. Builders reduce component weight and strengthen reliability, which lowers maintenance expenses across the vessel lifecycle.
- Restraint: High up-front production cost limits adoption across small and mid-size yards. Repair and recyclability concerns slow the transition toward composite-intensive designs in some regulated markets.
- Opportunity: New material systems that blend composite strength with renewable inputs open a path to higher sustainability ratings. Producers targeting epoxy alternatives and bio-resin blends position themselves for faster adoption in performance boats and coastal patrol vessels.
- Trend: Automation in resin infusion and filament winding strengthens throughput and limits labor shortages. Owens Corning, Toray Industries, and SGL Group expand R&D to advance fiber reinforcement, improve resin compatibility, and reduce total production cost.
- Regional Analysis: Asia Pacific leads with 42.6 percent share in 2023, supported by strong recreational boat production in China and South Korea. Europe and North America follow with steady demand from commercial fleets, naval upgrades, and expanding yacht manufacturing.
Type Analysis
The marine composites market continues to shift toward Polymer Matrix Composites in 2025. These materials hold the largest share due to their balance of structural strength, corrosion resistance, and cost control. You see strong uptake across hulls, decks, and internal structures as builders look for lighter components that support fuel efficiency targets. PMCs remain easier to process than metal or ceramic systems, which helps yards maintain predictable production schedules. Glass fiber stays the dominant reinforcement, accounting for more than half of PMC demand, while polyester resin gains traction because of its price advantage over epoxy and vinyl ester systems.
Ceramic Matrix Composites show the fastest growth outlook through 2030. Their stiffness, heat tolerance, and chemical resistance support broader adoption in performance vessels and specialty components. CMC held more than 30 percent share earlier in the decade and now expands as manufacturers qualify these materials for larger structures. Metal Matrix Composites continue to serve niche applications where higher temperature thresholds are required, though cost pressure limits their scale.
The overall type landscape reflects a clear push toward lighter builds and lower lifecycle costs. PMCs continue to anchor most volume due to their manufacturability and cost structure. CMC growth adds momentum in premium and high-load applications, giving producers a wider range of material options as vessel designs evolve.
Application Analysis
Marine composites gain stronger adoption in hulls, pavers, retaining walls, and structural elements that need corrosion resistance and extended service life. Pavers account for the largest application share as ports and marinas replace concrete blocks with composite units that resist saltwater exposure and require limited maintenance. Retaining walls follow similar adoption patterns as coastal infrastructure projects rise across Asia Pacific and North America.
Applications tied to vessel structures show steady expansion. Composites reduce weight in load-bearing areas and improve handling across fast craft and commercial fleets. Builders apply composite panels in decks, bulkheads, and exterior structures to limit corrosion and strengthen fatigue performance. These gains help you lower operating cost per vessel and meet tightening efficiency targets.
The application mix shifts further toward integrated composite systems by 2030. As resin infusion and automated lay-up methods improve, builders increase the share of composite components in both newbuilds and refurbishments.
End-Use Analysis
Residential and recreational segments continue to drive large portions of composite demand. Growth in personal watercraft and small leisure boats strengthens PMC consumption across hulls, masts, and interior structures. You see stronger activity in coastal markets with rising household spending and wider access to marinas.
Commercial buildings, ports, and marine terminals rely on composites to extend the lifespan of infrastructure exposed to saltwater and high humidity. These facilities adopt composite beams, panels, and structural wraps to reduce maintenance frequency and reinforce aging assets. Industrial end users invest in composites for chemical resistance and predictable performance in harsh environments, supporting steady demand across processing plants located near coastal zones.
Across all end-use sectors, the shift toward lightweight, corrosion-resistant materials accelerates as operators aim to extend service intervals and improve durability.
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific remains the largest regional market and accounts for more than 42 percent of global revenue in 2025. China, India, and South Korea continue to expand recreational boating access and marina development, which supports stronger demand for composite-intensive hulls and structural components. Shipyards across the region add new capacity to meet rising export orders for small and mid-size vessels.
Europe holds the second position with steady growth near 4 percent CAGR through the forecast period. The region’s shipbuilding base excels in complex vessels, submarines, and technical projects that rely heavily on composites. High manufacturing standards and strong regulatory requirements push builders to adopt materials that enhance structural reliability and reduce long-term cost.
North America follows as a mature but stable market. Spending on powerboats and high-performance craft remains strong due to high income levels and extensive coastal recreation. The region approaches USD 674 million in composite demand by 2025, supported by continued adoption in leisure vessels, refits, and coastal infrastructure upgrades.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportКеу Маrkеt Ѕеgmеntѕ
By Composites
- Ceramic Matrix Composites
- Metal Matrix Composites
- Polymer Matrix Composites
- Polymer Matrix Composites by Fabric Type
- Polymer Matrix Composites by Resin Type
By Resin Type
- Epoxy
- Polyster
- Other Resin Types
By Vessel Type
- Power Boats
- Racing Boats
- Yachts
- Catamarans
- Others
- Sailboats
- Cruise Ships
- Other Vessel Types
Region
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 5.3 billion |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 9.3 billion |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 5.8% |
| Historical data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | By Composites, (Ceramic Matrix Composites, Metal Matrix Composites, Polymer Matrix Composites, Polymer Matrix Composites by Fabric Type, Polymer Matrix Composites by Resin Type), Resin Type, (Epoxy, Polyster, Other Resin Types), By Vessel Type, (Power Boats, Racing Boats, Yachts, Catamarans, Others, Sailboats, Cruise Ships, Other Vessel Types) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Hyosung, Gurit Holding, Toray Industries Inc, 3A Composites, SGL Group, Teijin Limited, Owens Corning, Mitsubishi Rayon Co, Hexcel Corporation, Cytec Industries, E. I. Du Pont Nemours & Co, Others |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date