North America Generative AI in Testing Market Size, Trend | CAGR 33.91%
North America Generative AI in Testing Market Size, Share, Analysis Report Component (Software, Services), Deployment (Cloud, On-premises, Hybrid), Application (Automated Test Case Generation, Intelligent Test Data Creation, AI-Powered Test Maintenance, Predictive Quality Analytics, Technology, NL-to-Test, Agentic Orchestration, Vision & Model-Based UI Understanding, Retrieval-Augmented Testing, Test-Data Generators), Organization Size (Large Enterprises, SMEs), End Use (IT & Telecom, BFSI, Healthcare & Life Sciences, Retail & eCommerce, Manufacturing & Industrial, Public Sector & Education) Region and Key Players - Industry Segment Overview, Market Dynamics, Competitive Strategies, Trends and Forecast 2025-2034
Report Overview
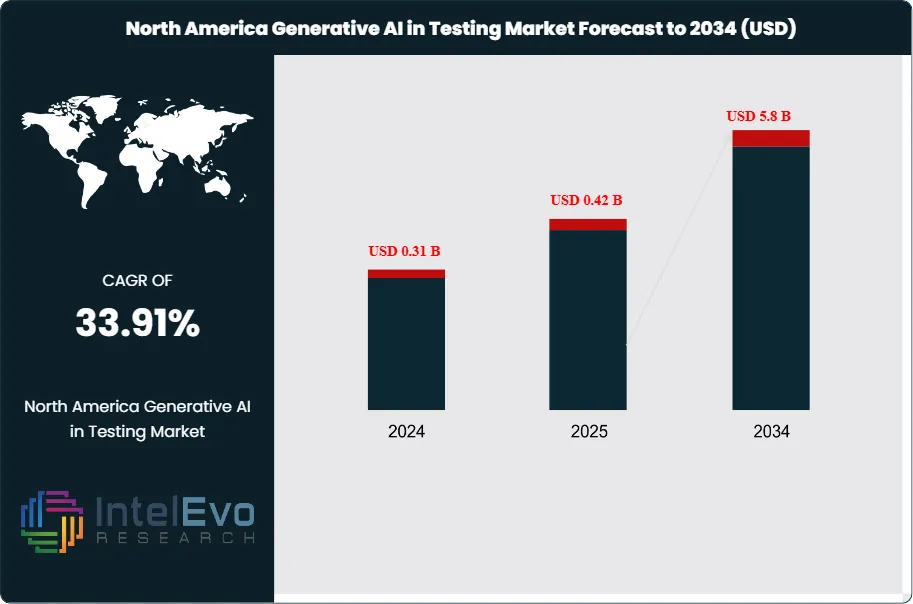
The North America Generative AI in Testing Market was valued at approximately USD 0.31 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach nearly USD 5.8 billion by 2034, driven by accelerating enterprise adoption of AI-powered test automation, DevOps integration, and cloud-native application development across the United States and Canada. Based on the stated growth trajectory, the market size for 2025 is estimated at approximately USD 0.42 billion. From 2025 onward, the market is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 33.91% during 2025–2034, ultimately reaching around USD 5.8 billion by 2034.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportThe region's adoption is mostly driven by software, which accounts for about 71% of spending. There is a strong preference for cloud delivery, nearly reaching 80%, due to benefits like flexible computing, quick updates, and easy scaling. Automated test-case generation makes up roughly 29% of the market. This reflects the need for converting plain language into tests, speeding up writing, and improving coverage without needing extensive scripting.
North America’s role as the leading market comes from its well-established cloud systems, effective CI/CD practices, and strong demand in IT and telecom, financial services, healthcare, and public programs. Teams are moving beyond pilot projects to regular use. Natural-language authoring helps reduce test backlogs, while synthetic data with privacy measures manages sensitive processes. Self-healing technology keeps fragile automation reliable as interfaces change. Predictive analytics focus on identifying risky code changes to reduce cycle times and increase defect detection rates.
Governance is seen as an essential part of design. Policies ensure model and version pinning, review checkpoints, redaction of sensitive fields, and audit trails for generated assets. Cloud-first rollouts speed up deployment for distributed teams, while hybrid setups manage restricted data locally without losing orchestration benefits. Integrating with requirement tracking, defect tracking, and development pipelines allows generative output to become a recognized, versioned asset in the QA workflow.
End-use activity is highest in sectors with frequent releases and high reliability demands. IT and telecom lead, followed by BFSI and healthcare, each leveraging GenAI to manage large test suites amid ongoing changes. While North America currently leads in adoption, Asia-Pacific is growing quickly; Europe is concentrating on compliance and explainability; and Latin America and North America and Africa are gaining ground through partner-driven rollouts.

Key Takeaways
- Market Size: USD 0.31B (2024) → USD 5.8B (2034) at ~33.91% CAGR (2025–2034).
- Component (Software): ~71% share in 2024, underscoring platform-led buying patterns.
- Deployment (Cloud): ~80% share in 2024, reflecting demand for elastic compute and managed updates.
- Application (Test Case Generation): ~29% share, driven by NL-to-test workflows that reduce scripting and raise coverage.
- End Use (IT & Telecom): ~34% share, aligned with high complexity and uptime demands.
- Driver: Advanced DevOps maturity and cloud infrastructure enable fast GenAI integration in QA.
- Restraint: Data residency rules, governance compliance, and integration complexity slow scale in regulated industries.
- Opportunity: BFSI and healthcare can leverage auditable generation with synthetic data to expand coverage for sensitive scenarios.
- Trend: Copilot-style authoring in IDEs, agentic orchestration linking UI/API/data flows, and risk-based regression testing.
Component Analysis
Software (about 71% in 2024): Spending focuses on platform capabilities that integrate generative AI into daily testing workflows. The main benefits include natural language to test authoring, self-healing maintenance, risk-based selection, and strong governance. Buyers prefer suites that connect with existing pipelines (like Git, CI/CD, issue trackers) and developer workspaces (IDEs) to ensure generated materials are versioned, reviewable, and traceable.
In highly regulated North American industries, software selection increasingly depends on provenance controls: who initiated what, with which model or version, and what evidence supports each statement. This focus on compliance, along with measurable improvements in authoring speed and suite stability, keeps software as the foundation.
Services (about 29%): Services make programs effective: they include systems integration, data governance and residency reviews, prompt pattern libraries, synthetic data safeguards, change management, and training for software developers in test roles and product teams. Advisory partners help measure ROI (like time saved in authoring, reductions in defect detection, and flaky test decreases) and establish approval gates so only well-supported tests are included in crucial suites. In North America, services also create hybrid reference architectures — using the cloud for flexible experimentation and analytics while maintaining on-prem/private systems for sensitive datasets — ensuring compliance with InfoSec requirements and preserving agility.
What shifts next: As buyers seek to consolidate tools, we see a trend toward platforms that combine test authoring, maintenance, data, and analytics under one governance model. Expect services to focus on runbooks and centers of excellence that allow business lines to adopt practices without needing custom solutions each time.
Deployment Analysis
Cloud (about 80% in 2024): Cloud remains the default because of its flexible computing, quick provisioning, and managed updates that keep models, policies, and connectors up to date. Elasticity is vital in North American release schedules: teams scale up for pre-release surges and then scale down. Cloud facilitates rollout to distributed engineering organizations, ensuring consistent policies across subsidiaries and vendors.
On-premises / Private Cloud (about 20%): Still crucial where data sensitivity, residency, latency, or network isolation are concerns. The banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) sector and public sector often handle prompt redaction, local inference, or last-mile validation in private domains. Many programs adopt a hybrid approach: using cloud for authoring, analytics, and model experimentation while keeping on-prem/private systems for limited logs, personally identifiable information (PII)-related data, and final checks.
What shifts next: Expect policy-as-code to spread across both deployment methods, unifying model pinning, data management, and audit trails. Procurement teams are increasingly looking for portable architectures — containerized inference and neutral connectors — to avoid lock-in while remaining cloud-first.
Application Analysis
Automated Test-Case Generation (about 29%): The most obvious near-term return on investment: converting user stories and requirements into runnable tests, reducing authoring time, and increasing coverage — especially valuable in fast-changing microservices and mixed SaaS plus custom environments.
AI-Powered Test Maintenance (Self-Healing) (about 20–22%): Keeps test suites functioning as selectors, flows, and responses change; recommended fixes are provided as differences along with evidence, and policy holds any unclear issues for human review. This is crucial for user interface-heavy applications that change frequently.
Intelligent Test Data Creation (Synthetic) (about 18–19%): Synthetic, constraint-aware data enables testing of previously untestable scenarios, such as those involving PII, protected health information (PHI), or payment card information (PCI). Adoption is increasing in BFSI and healthcare where privacy, data lineage, and differential risk are critical.
Predictive Quality Analytics (about 16–18%): Combines code changes, ownership, and historical failures to focus on high-risk areas, reducing regression while improving defect yield. It connects with continuous integration pipelines to select smarter subsets instead of larger groups.
Agentic Orchestration & Evaluation (around 12–15%): Multi-step agents manage data preparation, UI, and API in one step; offline evaluation processes outputs before they are promoted to critical suites — growing rapidly among teams standardizing on evidence-based governance.
End-Use Analysis
IT & Telecom (around 34%): Always-on services, high concurrency, and complex systems require aggressive automation and targeted regression testing. Generative AI helps simulate network and user variability to stabilize fragile processes as interfaces evolve. BFSI (about 21–23%): Security, compliance, and customer trust drive the use of these technologies. Synthetic data and auditable generation enhance coverage without exposing sensitive information. Generative AI stabilizes core banking, payment processes, and digital services.
Healthcare & Life Sciences (around 14–16%): Patient-facing portals, clinical workflows, and regulated documentation benefit from data that protects privacy and test assets that can be traced. Capturing evidence and pinning models and versions are essential. Public Sector & Education (approximately 10–12%): Modernizing digital services (like identity management, benefits portals, and permits) relies on hybrid deployment, stacks aligned with FedRAMP, and policy controls to pass audits. Retail/eCommerce (around 8–10%) & Manufacturing (about 5–7%): Omnichannel launches, promotions, and seasonal peaks require flexible testing environments; in manufacturing, product lifecycle management, manufacturing execution systems, and Internet of Things interfaces drive UI and API coordination.
Regional Dynamics (U.S. & Canada)
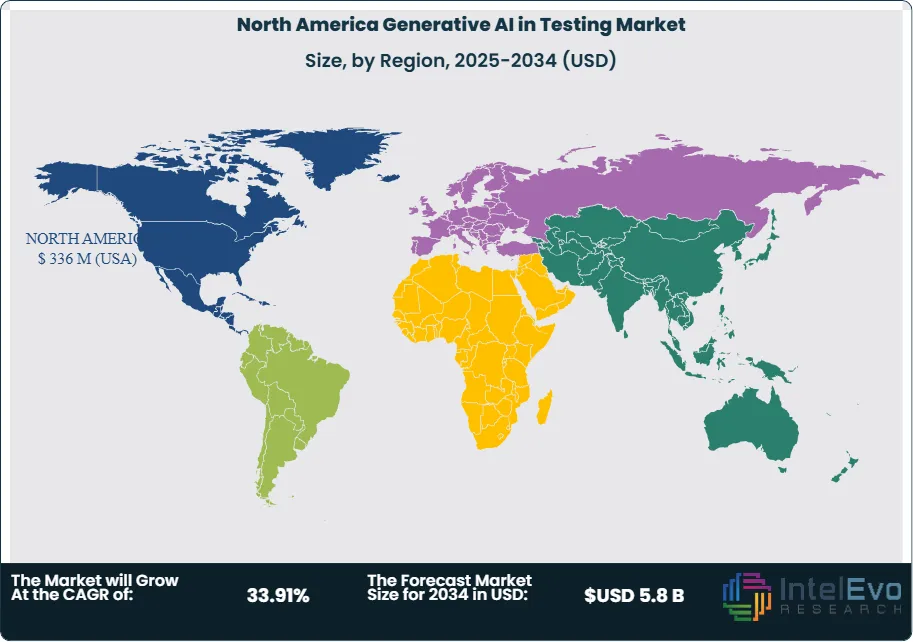
United States (about 88–90% of North American spending): Leads due to widespread cloud adoption, mature CI/CD engineering, and significant investment from BFSI, healthcare, and public services. U.S. programs generally follow a cloud-first approach, with hybrid systems for sensitive data, meeting HIPAA, PCI, SOX, and FedRAMP standards. Decision-making frameworks prioritize measurable ROI (like reduced defect leakage and improved suite stability) and verifiable governance.
Canada (about 10–12%): Strong uptake in public sector, healthcare, and fintech; there is substantial interest in data-residency-aware frameworks and privacy-focused engineering. Partner-led integrations speed up the time-to-value for provincial programs and large distributed organizations.
Momentum. As North America standardizes on assistants in development environments, agentic orchestration and evaluation tools, we observe a shift from exploratory tests to repeatable, policy-compliant operations with strict tracking of key performance indicators.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportKey Market Segment
Component
• Software
• Services
Deployment
• Cloud
• On-premises / Private Cloud
• Hybrid
Application
• Automated Test Case Generation
• Intelligent Test Data Creation (Synthetic)
• AI-Powered Test Maintenance (Self-Healing)
• Predictive Quality Analytics
Technology / Approach
• NL-to-Test (Code-LLMs, Copilot-style)
• Agentic Orchestration (multi-step workflows)
• Vision & Model-Based UI Understanding
• Retrieval-Augmented Testing (RAG for requirements/coverage)
• Test-Data Generators (tabular, time-series, anonymization)
Organization Size
• Large Enterprises
• SMEs
End Use
• IT & Telecom
• BFSI
• Healthcare & Life Sciences
• Retail & eCommerce
• Manufacturing & Industrial
• Public Sector & Education
Region
- North America
- U.S.A.
- CANADA
- Mexico
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2025) | USD 0.42 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 5.8 B |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 33.91% |
| Historical data | 2018-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | Component (Software, Services), Deployment (Cloud, On-premises / Private Cloud, Hybrid), Application (Automated Test Case Generation, Intelligent Test Data Creation (Synthetic), AI-Powered Test Maintenance (Self-Healing), Predictive Quality Analytics, Technology / Approach, NL-to-Test (Code-LLMs, Copilot-style), Agentic Orchestration (multi-step workflows), Vision & Model-Based UI Understanding, Retrieval-Augmented Testing (RAG for requirements/coverage), Test-Data Generators (tabular, time-series, anonymization)), Organization Size (Large Enterprises, SMEs), End Use (IT & Telecom, BFSI, Healthcare & Life Sciences, Retail & eCommerce, Manufacturing & Industrial, Public Sector & Education) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Tricentis, Keysight (Eggplant), Applitools, Functionize, Parasoft, SmartBear, Mabl, Katalon, Sauce Labs, BrowserStack, LambdaTest, OpenText (Micro Focus), IBM, Microsoft, TestSigma, Diffblue |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the North America Generative AI in Testing Market?
North America Generative AI in Testing market is set to grow from USD 0.31B in 2024 to USD 5.8B by 2034, at a CAGR of 33.91%. Explore trends, drivers, and opportunities.
Who are the major players in the North America Generative AI in Testing Market?
Tricentis, Keysight (Eggplant), Applitools, Functionize, Parasoft, SmartBear, Mabl, Katalon, Sauce Labs, BrowserStack, LambdaTest, OpenText (Micro Focus), IBM, Microsoft, TestSigma, Diffblue
Which segments covered the North America Generative AI in Testing Market?
Component (Software, Services), Deployment (Cloud, On-premises / Private Cloud, Hybrid), Application (Automated Test Case Generation, Intelligent Test Data Creation (Synthetic), AI-Powered Test Maintenance (Self-Healing), Predictive Quality Analytics, Technology / Approach, NL-to-Test (Code-LLMs, Copilot-style), Agentic Orchestration (multi-step workflows), Vision & Model-Based UI Understanding, Retrieval-Augmented Testing (RAG for requirements/coverage), Test-Data Generators (tabular, time-series, anonymization)), Organization Size (Large Enterprises, SMEs), End Use (IT & Telecom, BFSI, Healthcare & Life Sciences, Retail & eCommerce, Manufacturing & Industrial, Public Sector & Education)
How can this market research report help my business make strategic decisions?
Our market research reports provide actionable intelligence, including verified market size data, CAGR projections, competitive benchmarking, and segment-level opportunity analysis. These insights support strategic planning, investment decisions, product development, and market entry strategies for enterprises and startups alike.
How frequently is the data updated?
We continuously monitor industry developments and update our reports to reflect regulatory changes, technological advancements, and macroeconomic shifts. Updated editions ensure you receive the latest market intelligence.
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
North America Generative AI in Testing Market
Published Date : 20 Aug 2025 | Formats :Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date