Nuclear Medicine Market Outlook Size, Share & Growth | CAGR 11.12%
Global Nuclear Medicine Market Size, Share & Analysis By Product Type (Diagnostics, Therapeutics), By Application (Cardiology, Oncology, Neurology, Thyroid, Lymphoma, Bone Metastasis, Urology, Pulmonary Scans, Endocrine Tumor, Other), By End-user (Hospitals, Diagnostic Centers), Technology Advancements, Regulatory Outlook & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
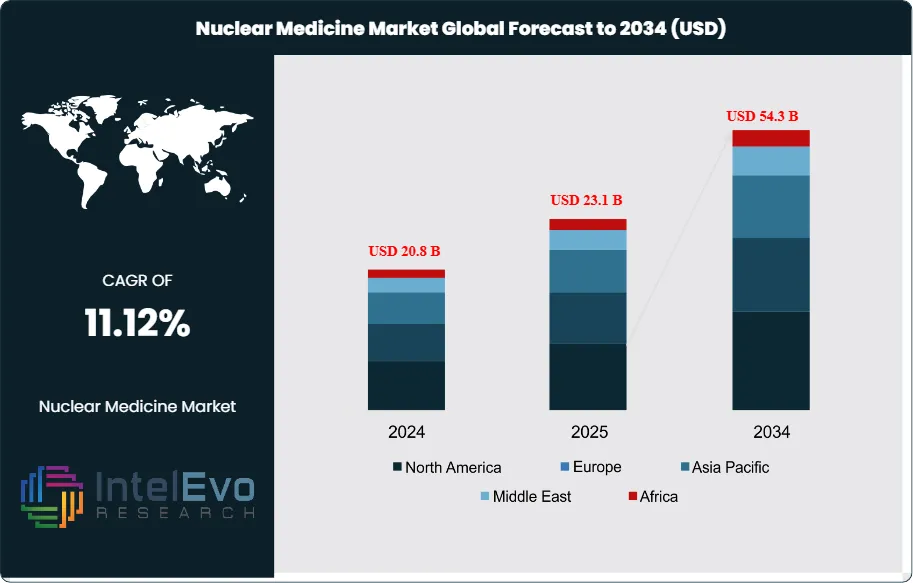
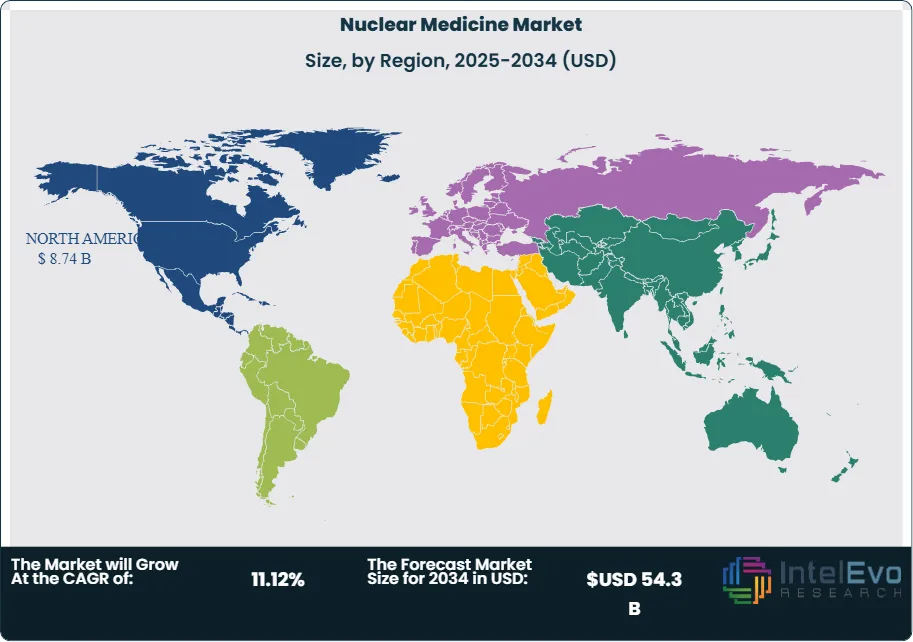
The Nuclear Medicine Market size is expected to be worth around USD 54.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 20.8 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 11.12% during 2025–2034. This growth trajectory underscores the critical role nuclear medicine plays in modern healthcare, particularly in addressing the global rise in chronic diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders. In 2024, North America accounted for more than 43.5% of the market, valued at USD 8.4 Billion, supported by strong healthcare infrastructure, high adoption of advanced imaging technologies, and significant research investments.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportThe escalating incidence of cancer worldwide is a primary driver of market demand. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there were nearly 20 million new cancer cases and 9.7 million cancer-related deaths in 2022, underscoring the need for precise and effective diagnostic and therapeutic tools. Nuclear medicine offers unique value in this context by enabling molecular-level imaging and targeted radiotherapy, which enhances treatment outcomes while minimizing damage to healthy tissues. Its role is particularly vital for long-term cancer management, as advanced imaging systems facilitate ongoing monitoring and earlier disease detection.
Technological advancements are accelerating adoption across both diagnostic and therapeutic domains. The integration of hybrid imaging systems such as PET/CT and SPECT/CT is improving diagnostic accuracy and supporting earlier intervention strategies. Meanwhile, the rise of theranostics—an approach that combines diagnostic scans with targeted therapeutic doses—is reshaping oncology by enabling personalized treatment regimens tailored to individual patient profiles. Growing regulatory support, such as the U.S. FDA’s draft guidance on optimizing dosage for oncology radiopharmaceuticals, reflects the shift toward precision medicine and more effective therapeutic outcomes.
Innovation in radiopharmaceuticals is further broadening the scope of nuclear medicine. Companies are developing next-generation agents designed to target diverse molecular pathways, expanding the applicability of these treatments beyond oncology into cardiology, neurology, and other chronic disease areas. Strategic partnerships between pharmaceutical firms, research institutions, and healthcare providers are accelerating product development and commercialization, while government support through initiatives led by organizations such as the NIH and DOE continues to strengthen the research ecosystem.
Globally, over 10,000 hospitals were reported to use medical radioisotopes in 2024, with nearly 90% of these procedures employed for diagnostics. This widespread usage highlights nuclear medicine’s indispensable role in healthcare delivery. Looking ahead, the convergence of technological innovation, personalized medicine, and sustained public and private sector investment will continue to drive the market’s expansion, reinforcing nuclear medicine as a cornerstone of next-generation healthcare solutions.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The global Nuclear Medicine Market generated USD 20.8 Billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 54.3 Billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 11.2%. Expansion is driven by rising cancer prevalence, increased use of molecular imaging, and broader adoption of targeted radiotherapies.
- Product Type: Diagnostic nuclear medicine dominated with a 74.6% share in 2024, supported by widespread use of PET and SPECT imaging in oncology, cardiology, and neurology for early disease detection and monitoring.
- Application: Urology accounted for the largest application share at 34.1%, reflecting the increasing use of radiopharmaceuticals in prostate cancer diagnosis and treatment, alongside strong adoption of theranostic approaches in managing urological conditions.
- End User: Hospitals held the leading position with 60.5% market share, benefiting from integrated imaging departments, advanced infrastructure, and the ability to deliver both diagnostic and therapeutic nuclear medicine services under one roof.
- Driver: Rising global cancer incidence and the demand for precision therapies are accelerating uptake of nuclear medicine, with theranostics emerging as a major driver of personalized treatment strategies.
- Restraint: High production costs of radiopharmaceuticals, short half-lives of isotopes, and the need for specialized facilities continue to limit accessibility, particularly in developing regions.
- Opportunity: Development of next-generation radiopharmaceuticals and radionuclide therapies targeting new molecular pathways presents significant growth potential, especially in expanding applications beyond oncology into cardiology and neurology.
- Trend: The integration of hybrid imaging systems (PET/CT, SPECT/CT) and the rapid rise of theranostic solutions are reshaping the market, enabling earlier diagnosis and highly tailored treatment approaches that align with the shift toward precision medicine.
Product Type Analysis
In 2025, diagnostic nuclear medicine remains the dominant category, accounting for nearly three-fourths of overall revenues. The segment’s strength stems from the widespread clinical use of positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) in oncology, cardiology, and neurology. These imaging tools provide unparalleled insights into organ function and disease progression, offering advantages over conventional modalities. The increasing global burden of cancer and cardiovascular diseases continues to reinforce demand for diagnostic applications.
Advances in imaging precision and resolution, combined with hybrid systems that integrate PET/CT and SPECT/CT, are further strengthening adoption. Healthcare providers are prioritizing early detection and preventive care, making nuclear diagnostics a critical part of patient management. With emerging economies now expanding their access to advanced imaging infrastructure, the global adoption of diagnostic nuclear medicine is expected to accelerate steadily over the next decade.
In contrast, the therapeutics segment—including alpha emitters, beta emitters, and brachytherapy—is gaining momentum as targeted radionuclide therapies become more mainstream. These treatments deliver radiation directly to diseased cells while sparing healthy tissues, making them a key driver of precision oncology. Growing clinical evidence and regulatory approvals for targeted radiopharmaceuticals are anticipated to expand this segment’s role significantly through 2034.
By Application Analysis
Urology leads the nuclear medicine market by application, representing more than one-third of global revenues in 2025. This dominance is largely driven by the rising prevalence of prostate cancer and the rapid adoption of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-based imaging and therapy. Nuclear medicine techniques are increasingly being used for both diagnosis and therapy in urological conditions, including kidney and bladder cancers, as they enable accurate disease staging and monitoring of treatment efficacy.
Oncology more broadly remains one of the fastest-growing application areas, as theranostic approaches allow for tailored treatment plans based on individual tumor profiles. Cardiology and neurology also represent important use cases, with nuclear imaging widely applied in the assessment of heart perfusion and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease. The diversification of radiopharmaceutical pipelines toward endocrine tumors, lymphoma, and pulmonary conditions demonstrates the widening scope of nuclear medicine beyond its traditional strongholds.
End-User Analysis
Hospitals remain the largest end-user segment, accounting for more than 60% of global demand in 2025. These facilities are the primary centers for both diagnostic imaging and therapeutic nuclear medicine due to their access to advanced infrastructure, specialist expertise, and patient volumes. With cancer and cardiovascular cases increasing globally, hospitals continue to be the frontline for adopting PET and SPECT technologies, as well as for administering radionuclide therapies.
The integration of nuclear medicine into treatment pathways—such as disease staging, therapy planning, and monitoring outcomes—has further cemented hospitals’ dominance. Investment in cutting-edge equipment and the expansion of outpatient imaging departments are expected to sustain this leadership. Meanwhile, diagnostic centers are emerging as strong secondary players, offering specialized services with faster turnaround times, particularly in urban markets. As accessibility improves, smaller treatment centers and private diagnostic labs are expected to play a growing role in extending nuclear medicine to wider populations.
Regional Analysis
North America remains the global leader in nuclear medicine, holding over 42% of total market share in 2025. The region benefits from advanced healthcare infrastructure, early adoption of novel radiopharmaceuticals, and substantial R&D investments. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) continues to accelerate market access through approvals of next-generation radiopharmaceuticals, supporting rapid integration into clinical practice. The significant cancer burden in the U.S., with over 2 million new cases estimated in 2025, ensures sustained demand for both diagnostic and therapeutic nuclear medicine.
Asia Pacific is projected to record the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. Countries such as China and India are witnessing surging cancer incidence rates, coupled with expanding healthcare spending and government-backed initiatives to improve access to advanced medical technologies. For example, India’s rising public health budget allocations are enhancing imaging infrastructure and radiotherapy facilities across major cities. The large, aging population in the region is also fueling demand for both diagnostic imaging and therapeutic solutions.
Europe continues to demonstrate strong adoption, supported by a growing focus on personalized medicine and stringent clinical guidelines that promote advanced imaging in oncology and cardiology. Meanwhile, the Middle East & Africa and Latin America are emerging markets, where rising investments in healthcare infrastructure and partnerships with global radiopharmaceutical companies are expanding access to nuclear medicine. These regions represent untapped potential as demand for cancer care and non-invasive diagnostics continues to rise.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportMarket Key Segments
By Product Type
- Diagnostics
- SPECT
- TL-201
- TC-99m
- I-123
- GA-67
- Others
- PET
- SR-82/RB-82
- PYLARIFY
- Illuccix
- F-18
- Others
- SPECT
- Therapeutics
- Alpha Emitters
- RA-223
- Others
- Beta Emitters
- Y-90
- SM-153
- Re-186
- Lu-177
- I-131
- Others
- Brachytherapy
- Palladium-103
- Iridium-192
- Iodine-125
- Cesium-131
- Others
- Alpha Emitters
By Application
- Cardiology
- SPECT
- PET
- Therapeutic Applications
- Oncology
- SPECT
- Therapeutic Applications
- Neurology
- Thyroid
- Lymphoma
- Bone Metastasis
- Urology
- Pulmonary Scans
- Endocrine Tumor
- Other
By End-user
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic Centers
Regions
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 20.8 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 54.3 B |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 11.12% |
| Historical data | 2020-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | By Product Type (Diagnostics, Therapeutics), By Application (Cardiology, Oncology, Neurology, Thyroid, Lymphoma, Bone Metastasis, Urology, Pulmonary Scans, Endocrine Tumor, Other), By End-user (Hospitals, Diagnostic Centers) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | The institute for radioelements, The Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization, NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd, Nordion (Canada), Inc, Mallinckrodt, Lantheus Medical Imaging, Inc, Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd, GE Healthcare, Eczacıbaşı-Monrol, Eckert & Ziegler, Cardinal Health, Bracco Imaging S.P.A |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Frequently Asked Questions
How big is the Nuclear Medicine Market?
The Nuclear Medicine Market will reach USD 54.3 Bn by 2034 from USD 20.8 Bn in 2024, driven by rising cancer cases, cardiac disorders & advanced imaging demand.
Who are the major players in the Nuclear Medicine Market?
The institute for radioelements, The Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization, NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd, Nordion (Canada), Inc, Mallinckrodt, Lantheus Medical Imaging, Inc, Jubilant Life Sciences Ltd, GE Healthcare, Eczacıbaşı-Monrol, Eckert & Ziegler, Cardinal Health, Bracco Imaging S.P.A
Which segments covered the Nuclear Medicine Market?
By Product Type (Diagnostics, Therapeutics), By Application (Cardiology, Oncology, Neurology, Thyroid, Lymphoma, Bone Metastasis, Urology, Pulmonary Scans, Endocrine Tumor, Other), By End-user (Hospitals, Diagnostic Centers)
How can this market research report help my business make strategic decisions?
Our market research reports provide actionable intelligence, including verified market size data, CAGR projections, competitive benchmarking, and segment-level opportunity analysis. These insights support strategic planning, investment decisions, product development, and market entry strategies for enterprises and startups alike.
How frequently is the data updated?
We continuously monitor industry developments and update our reports to reflect regulatory changes, technological advancements, and macroeconomic shifts. Updated editions ensure you receive the latest market intelligence.
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date