Open RAN Market Size, Share, Trends & Forecast 2025–2034 | 32.9% CAGR
Global Open RAN Market Size, Share, Analysis Report By Component (Software, Hardware, Services), Network Type (5G Networks, 4G Networks, 2G/3G Networks), Unit (Centralized Unit, Radio Unit, Distributed Unit), Frequency (Millimeter Wave (mmWave), Sub-6 GHz) Industry Region & Key Players-Industry Segment Overview, Market Dynamics, Competitive Strategies, Trends & Forecast 2025-2034
Report Overview
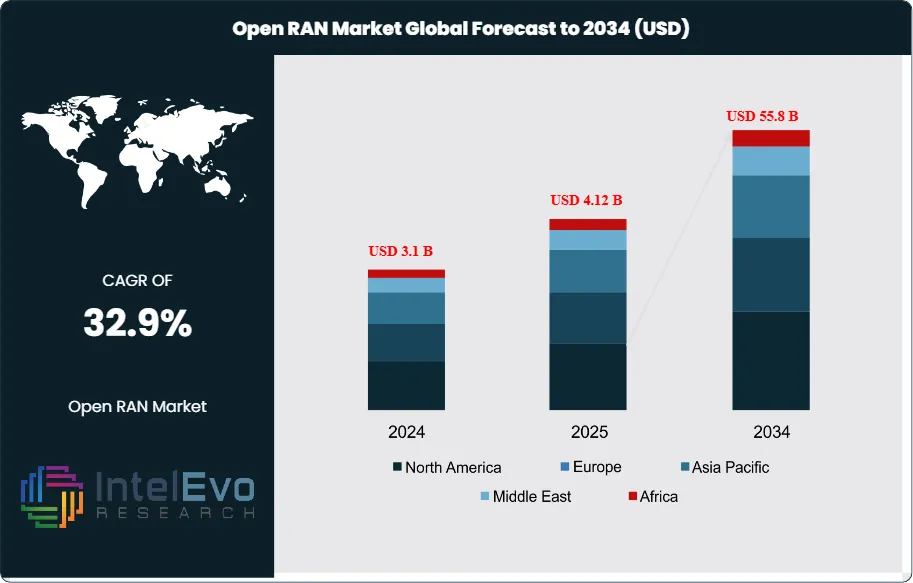
The Open RAN Market size is expected to be worth around USD 55.8 Billion by 2034, up from USD 3.1 Billion in 2024, growing at a robust CAGR of 32.9% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2034. The Open RAN market is witnessing remarkable momentum as telecom operators embrace network disaggregation, cost-efficient infrastructure, and multi-vendor interoperability. With 5G rollout accelerating globally and open network architectures gaining mainstream adoption, the demand for Open RAN solutions is expected to surge dramatically over the next decade. This shift marks a significant move toward innovation, flexibility, and reduced dependency on traditional network vendors — positioning Open RAN as a transformative force in next-generation telecommunications.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportOpen Radio Access Network (Open RAN) represents a paradigm shift in telecommunications infrastructure, enabling interoperability between hardware and software components from different vendors through standardized interfaces.
The market encompasses the transformation of traditional RAN architecture into a disaggregated, cloud-native network that promotes vendor diversification and innovation. The global open RAN market size was valued at USD 2.39 billion in 2024 and is expected to hit around USD 38.71 billion by 2034 with a CAGR of 32.11%. Key factors driving this growth include the accelerating 5G deployment worldwide, increasing demand for network flexibility, cost optimization pressures on telecom operators, and government initiatives promoting vendor diversification to reduce supply chain dependencies on single vendors.
The market is significantly influenced by technological advancements in cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and edge computing, which enable more efficient network management and optimization. Regulatory policies favoring open standards and interoperability, particularly in developed markets, are creating favorable conditions for Open RAN adoption. Additionally, the growing emphasis on network security and resilience, coupled with the need for reduced operational expenditures, is compelling operators to explore Open RAN solutions. The integration of machine learning and AI capabilities into RAN operations is enhancing network performance and enabling predictive maintenance, further accelerating market growth.
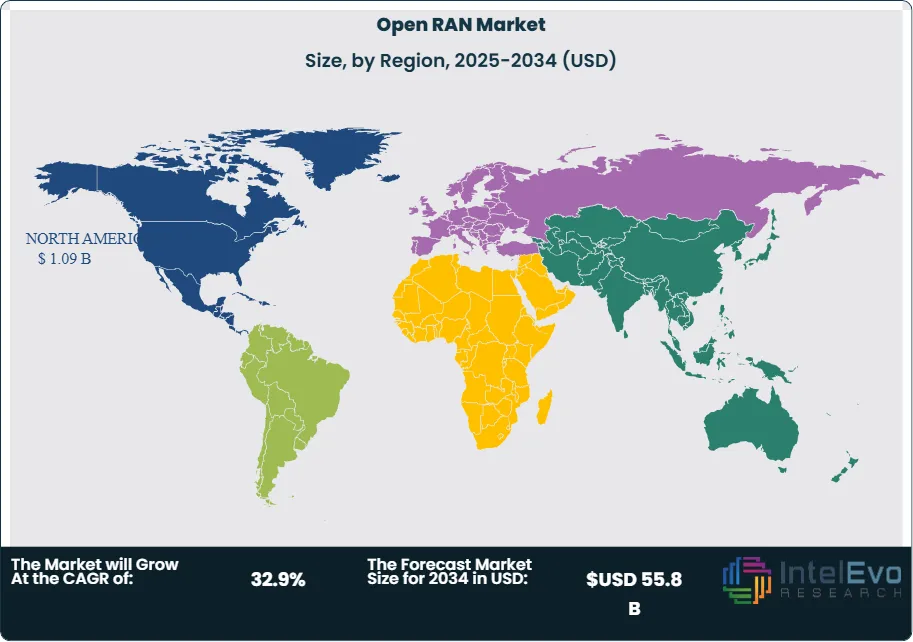
The regional analysis reveals that North America dominates the Open RAN market landscape, driven by substantial government investments, supportive regulatory frameworks, and the presence of major technology companies. North America leads the market in 2024, accounting for around 35% of the share, driven by strong telecom investments and government support. The region benefits from early adoption initiatives and significant funding for research and development in open networking technologies.
The COVID-19 pandemic initially disrupted the Open RAN market due to supply chain constraints and delayed network deployments. However, the crisis simultaneously accelerated digital transformation initiatives and highlighted the importance of resilient, flexible network infrastructure. The pandemic-driven surge in data traffic and remote work requirements emphasized the need for scalable, cost-effective network solutions, ultimately benefiting the Open RAN market's long-term growth trajectory.
Regional conflicts between major economies and ongoing trade tensions have significantly impacted the Open RAN market dynamics. The US-China trade war and subsequent technology restrictions have created opportunities for Open RAN vendors as operators seek to diversify their supply chains. Government initiatives such as the CHIPS Act in the United States and similar policies in Europe have allocated substantial funding to promote domestic semiconductor manufacturing and reduce dependence on Asian suppliers. These geopolitical tensions have led to increased tariffs on telecom equipment, making Open RAN solutions more attractive as they offer vendor-agnostic alternatives. The establishment of trusted vendor lists and security requirements for critical infrastructure has further accelerated Open RAN adoption, as operators seek compliant solutions that meet stringent security standards while maintaining operational efficiency.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Open RAN Market is expected to reach USD 55.8 Billion by 2034, propelled by 5G network expansion, cost optimization imperatives, and government-backed initiatives favoring open architectures.
- Component Dominance: Hardware remains the leading component segment due to the need for substantial investments in radios, centralized units, and distributed units during initial deployment phases.
- Network Type Dominance: 4G network upgrades dominate current Open RAN installations as operators retrofit existing infrastructure to prepare for 5G while maximizing prior investments.
- Unit Dominance: Among units, Radio Units command the largest share, as they are critical for transmitting and receiving signals across network frequencies.
- Frequency Dominance: Sub-6 GHz frequencies are the most widely adopted due to their balance of propagation range and capacity, enabling coverage in both urban and suburban areas.
- Driver: The key driver is the demand for cost-efficient, vendor-agnostic network infrastructure that can be rapidly deployed and scaled to meet evolving traffic demands.
- Restraint: One major restraint is the lack of mature interoperability standards, which complicates integration and slows down adoption.
- Opportunity: Open RAN offers operators unprecedented flexibility to deploy tailored network configurations and integrate AI-powered automation, creating strong business cases for investment.
- Trend: A significant trend is the shift towards virtualized RAN and cloud-native architectures that leverage edge computing for lower latency and enhanced performance.
- Regional Analysis: North America leads the market, thanks to substantial investment and favorable policies supporting Open RAN deployments. Europe is also progressing rapidly with government funding, while Asia Pacific is driven by pioneering efforts in Japan and South Korea.
Component Analysis
Hardware is the backbone of any Open RAN deployment. Radios, centralized units (CUs), and distributed units (DUs) collectively account for the largest share of investments because they form the physical infrastructure that transmits and processes signals. Hardware spending remains high as operators modernize legacy base stations and extend coverage for 4G and 5G services. Leading vendors such as Samsung, Nokia, and Ericsson are offering modular hardware that supports both legacy and next-generation networks. The focus on interoperability means operators procure hardware designed to integrate seamlessly with open software stacks. While the long-term trend is toward software-centric architectures, hardware remains critical for initial rollouts and is expected to maintain its leadership in the near term.
Network Type Analysis
Despite the hype surrounding 5G, most current Open RAN deployments are targeting 4G networks. This is largely because upgrading existing 4G infrastructure provides a more immediate return on investment, enabling operators to extend the lifespan of their networks while preparing for eventual 5G upgrades. Operators in emerging markets also prefer 4G because of the cost advantages and the wider device ecosystem. By implementing Open RAN in 4G, companies can reduce vendor lock-in and lower operational expenditures before making larger 5G investments. This segment will continue to dominate in the short term, especially in regions where 5G spectrum auctions are still underway.
Unit Analysis
Radio Units (RUs) are essential for transmitting and receiving signals between mobile devices and the network core. They account for the largest share of unit-level spending because each cell site requires multiple radios configured to operate on different frequency bands. Open RAN introduces standardized interfaces, enabling operators to mix and match radio hardware from various vendors. The demand for advanced radios that can support Sub-6 GHz and mmWave simultaneously is rising, further boosting this segment. Companies like Fujitsu, NEC, and Samsung have developed innovative RU solutions designed for flexible deployment across urban and rural environments.
Frequency Analysis
Sub-6 GHz frequencies are by far the most deployed spectrum bands in Open RAN networks due to their balanced performance characteristics. While millimeter wave offers higher bandwidth, Sub-6 GHz provides broader coverage and better indoor penetration, making it more suitable for large-scale deployments. This segment’s dominance is also reinforced by regulatory decisions that prioritize Sub-6 GHz spectrum allocations in most countries. As operators look to scale their networks cost-effectively, Sub-6 GHz remains the preferred choice for early and mid-phase Open RAN rollouts.
Region Analysis
North America Leads With 35% Market Share In Open RAN Market. North America maintains its leadership position in the Open RAN market, accounting for approximately 35% of global market share, driven by substantial government investments, supportive regulatory frameworks, and early adoption initiatives by major telecommunications operators. The region benefits from the presence of leading technology companies, advanced research institutions, and comprehensive funding programs such as the CHIPS Act and National Telecommunications and Information Administration grants. Europe follows with significant market share, supported by regulatory initiatives promoting open standards and vendor diversification. The European market is characterized by collaborative research programs and standardization efforts through organizations like the European Telecommunications Standards Institute.
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region, driven by massive 5G deployments, increasing smartphone penetration, and government initiatives promoting digital transformation. Countries like Japan and South Korea are leading Open RAN trials and deployments, while India presents significant growth opportunities due to its large telecommunications market and cost-sensitive operator requirements. The region's growth is supported by local manufacturing capabilities and increasing investment in telecommunications infrastructure.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportKey Market Segment
Component
- Software
- Hardware
- Services
Network Type
- 5G Networks
- 4G Networks
- 2G/3G Networks
Unit
- Centralized Unit
- Radio Unit
- Distributed Unit
Frequency
- Millimeter Wave (mmWave)
- Sub-6 GHz
Region
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2025) | USD 4.12 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 55.8 B |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 32.9% |
| Historical data | 2018-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | Component: (Software, Hardware, Services) Network Type: (5G Networks, 4G Networks, 2G/3G Networks) Unit: (Centralized Unit, Radio Unit, Distributed Unit) Frequency: (Millimeter Wave (mmWave), Sub-6 GHz) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Radisys Corporation (Reliance Industries), Rakuten Group, Inc., AT&T Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., ZTE Corporation, Nokia Corporation Finland, Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson, 1VIAVI Solutions Inc., Fujitsu Limited Japan, Mavenir, NEC Corporation, Parallel Wireless |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date