Power Transformer Market to Hit $49.3B by 2034 | CAGR 6.8%
Global Power Transformer Market Size, Share, Analysis By Report Power Output (Power Transformers(Small, Medium, Large)), Transformers' Cooling Type (Oil-Cooled, Air-Cooled), Transformers' Phase (Single, Three), Application (Power Generation Plants, Transmission and Distribution Utilities, Industrial Sector, Renewable Energy Integration) Industry Region & Key Players-Industry Segment Overview, Market Dynamics, Competitive Strategies, Trends & Forecast 2025-2034
Report Overview
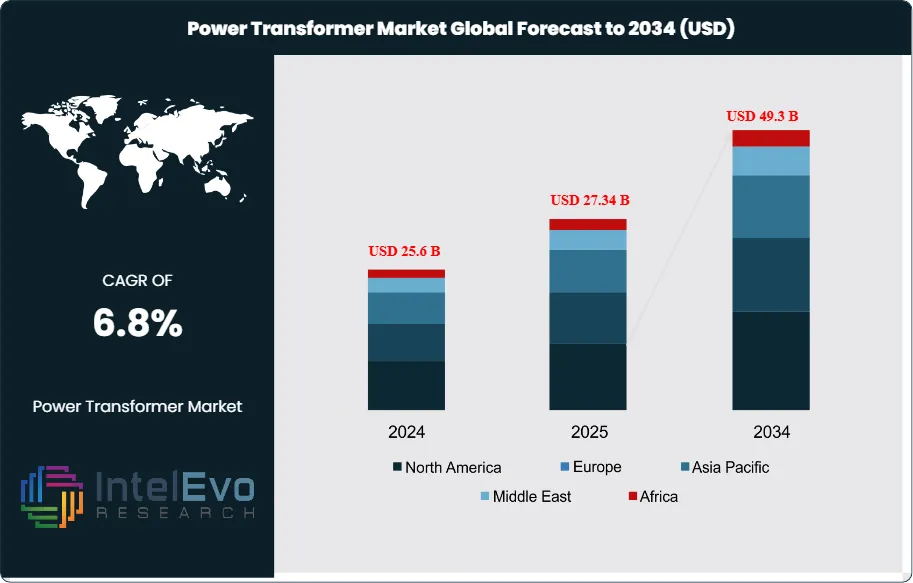
The Power Transformer Market size is expected to be worth around USD 49.3 Billion by 2034, from USD 25.6 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.8% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2034. The Global Power Transformer Market is a critical segment of the electrical equipment industry, encompassing the design, manufacturing, and deployment of large-scale transformers that facilitate the efficient transmission and distribution of electricity across vast distances. Power transformers are indispensable for modern power grids, as they enable the step-up of voltage for long-distance transmission from generation plants and the step-down of voltage for safe distribution to homes, businesses, and industries. The market is segmented by rating or power output into small (up to 60 MVA), medium (61–600 MVA), and large (above 600 MVA) power transformers. Small transformers are typically used in local distribution and rural electrification, medium transformers serve regional transmission and urban infrastructure, while large transformers are vital for high-voltage transmission networks, cross-border interconnections, and integrating bulk power from major generation sources, including renewables.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportBy application, the market is divided into power generation plants, transmission and distribution utilities (which hold the largest share due to ongoing grid modernization and expansion), industrial sectors (supporting high-load operations and manufacturing), and renewable energy integration (addressing the growing need to connect wind, solar, and other clean energy sources to the grid). Regionally, the market is led by Asia-Pacific, which commands the largest share owing to rapid urbanization, industrialization, and massive investments in grid infrastructure, particularly in China and India. These countries are aggressively expanding their transmission networks, electrifying rural areas, and integrating renewable energy at scale. Europe follows, driven by ambitious decarbonization targets, cross-border grid projects, and advanced smart grid initiatives, while North America focuses on grid resilience, modernization, and renewable integration. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are emerging as high-potential markets, propelled by infrastructure development, economic diversification, and efforts to improve electricity access.
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant but temporary impact on the power transformer market. In the early stages, global supply chains were disrupted, manufacturing was delayed, and many infrastructure projects were postponed as governments-imposed lockdowns and redirected resources to public health. However, the market demonstrated resilience, rebounding as countries recognized the importance of reliable electricity for economic recovery, digital transformation, and public health. Post-pandemic, there has been a renewed focus on grid modernization, digitalization, and the integration of renewable energy, all of which require advanced transformer solutions. Geopolitical factors also exert a profound influence on the market. Trade tensions, such as tariffs on steel, copper, and other raw materials, can increase production costs and disrupt supply chains, affecting both manufacturers and end-users. Regional conflicts and political instability can delay projects and create uncertainty in investment decisions. On the other hand, global policy shifts toward decarbonization and energy security are driving investments in smart grids, cross-border interconnections, and renewable energy integration, further shaping market dynamics. As a result, the global power transformer market is characterized by both challenges and opportunities, with its growth trajectory closely linked to technological innovation, regulatory developments, and the evolving geopolitical and economic landscape. The sector’s future will be defined by its ability to adapt to these changes, deliver reliable and efficient solutions, and support the world’s transition to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The Global Power Transformer Market is projected to reach approximately USD 49.3 billion by 2034, fueled by grid modernization initiatives, rising electricity demand, and the integration of renewable energy sources worldwide.
- Rating/Power Output Dominance: Large power transformers (above 600 MVA) dominate the market by value, as they are essential for high-voltage transmission, cross-border interconnections, and supporting bulk power transfer from major generation sources, including renewables.
- Application Dominance: Transmission and distribution utilities represent the largest application segment, accounting for about 50% of market share, as utilities invest heavily in upgrading aging infrastructure, expanding grid capacity, and integrating smart grid technologies.
- Drivers: Key drivers accelerating market growth include the global push for grid modernization, rapid urbanization and industrialization (especially in Asia-Pacific), and the increasing need for reliable, efficient integration of renewable energy into national grids.
- Restraints: Market expansion is challenged by high initial investment costs, long lead times for custom-built transformers, and volatility in raw material prices, which can impact project budgets and timelines.
- Opportunities: The market is poised for further growth through opportunities such as the adoption of smart grid and digital transformer technologies, expansion in emerging markets, and the rising demand for transformers tailored to renewable energy integration.
- Trends: Notable trends include the deployment of smart transformers with digital monitoring and predictive maintenance, the shift toward eco-friendly and energy-efficient designs, and increased investment in grid resilience and cross-border interconnections.
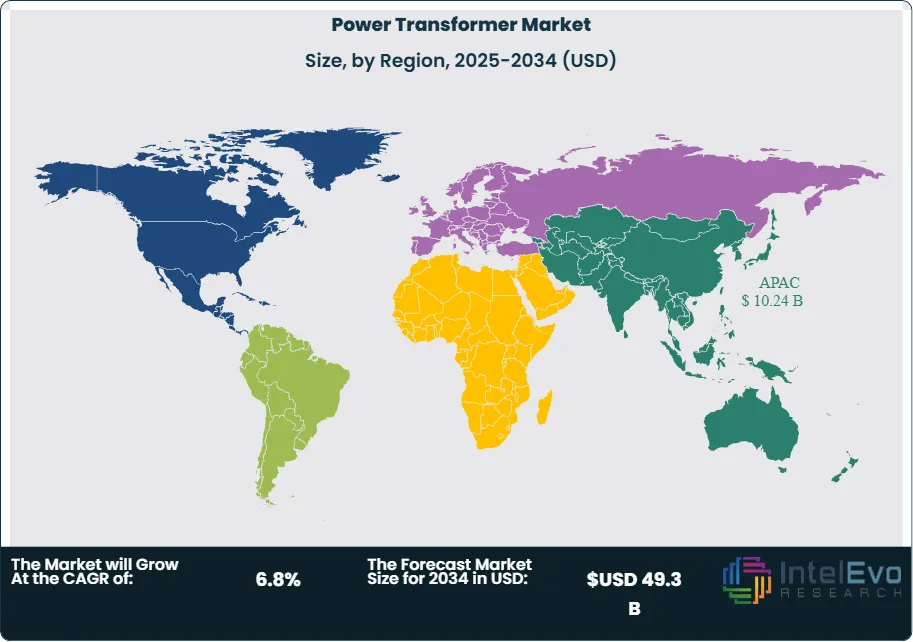
- Regional Analysis: Asia-Pacific leads the global market with approximately 40% share, driven by massive infrastructure investments in China and India. North America and Europe follow, focusing on grid modernization and decarbonization, while Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are emerging as high-growth regions due to electrification and infrastructure development.
Rating/Power Output Analysis
Large Power Transformers rated above 600 MVA, these are critical for high-voltage transmission and large-scale power generation. They are indispensable for national grids, cross-border interconnections, and integrating bulk power from major sources, including renewables. Large power transformers command the maximum share, accounting for about 45% of the market by value, due to their high cost and essential role in grid stability and long-distance transmission. Small Power Transformers these units, typically rated up to 60 MVA, are used for local distribution and small-scale industrial applications. They are essential for rural electrification and residential networks, but account for a smaller portion of the market—approximately 20%—due to their lower capacity and value compared to larger units. Medium Power Transformers with ratings between 61 MVA and 600 MVA, medium power transformers serve regional transmission and sub-transmission networks, urban infrastructure, and industrial complexes. They strike a balance between capacity and flexibility, holding a significant market share of around 35% as they are widely used in both distribution and transmission upgrades, especially in developing economies.
Application Analysis
Transmission and Distribution Utilities is the largest application segment, holding the maximum share of approximately 50%. Utilities depend on power transformers for reliable electricity transmission and distribution, grid modernization, and smart grid integration. The need to replace aging infrastructure and expand networks to meet rising demand sustains this segment’s dominance. Power Generation Plants transformers in this segment step up voltage for efficient long-distance transmission from power plants, including thermal, hydro, nuclear, and renewables. This segment represents about 22% of the market, driven by ongoing investments in new generation capacity and grid-connected renewable projects. Transmission and Distribution Utilities is the largest application segment, holding the maximum share of approximately 50%. Utilities depend on power transformers for reliable electricity transmission and distribution, grid modernization, and smart grid integration. The need to replace aging infrastructure and expand networks to meet rising demand sustains this segment’s dominance.
Industrial Sector require robust transformers for high-load operations, voltage stability, and uninterrupted power supply. The industrial segment accounts for about 18% of the market, with growth fueled by expanding manufacturing, data centers, and heavy industries, especially in emerging markets. Renewable Energy Integration as the world accelerates its shift to clean energy, transformers designed for integrating wind, solar, and other renewables are in high demand. This segment is rapidly growing and now represents around 10% of the market, with further expansion expected as decarbonization efforts intensify globally.
Region Analysis
Asia-Pacific commands the maximum regional share, at approximately 40%. Rapid urbanization, industrialization, and massive investments in power infrastructure—especially in China and India—make this the most dynamic and fastest-growing market for power transformers. North America mature market with steady investments in grid modernization and renewables, North America holds about 20% of the global market share. The U.S. leads the region, focusing on grid resilience and infrastructure upgrades. Europe accounts for roughly 23% of the market, driven by ambitious decarbonization targets, cross-border grid projects, and advanced smart grid initiatives. Countries like Germany, France, and the UK are at the forefront of these developments.
Latin America with ongoing infrastructure development and increasing electricity access, Latin America represents about 9% of the market. Brazil and Mexico are the primary contributors, focusing on grid upgrades and renewable integration. Middle East & Africa region holds around 8% of the market, with growth driven by economic diversification, urban development, and large-scale energy projects, particularly in the Middle East and emerging African economies.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportKey Market Segment
Rating/Power Output
- Small Power Transformers
- Medium Power Transformers
- Large Power Transformers
Cooling Type
- Oil-Cooled Transformers
- Air-Cooled (Dry-Type) Transformers
Phase
- Single-Phase Transformers
- Three-Phase Transformers
Application
- Power Generation Plants
- Transmission and Distribution Utilities
- Industrial Sector
- Renewable Energy Integration
Region:
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2025) | USD 27.34 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 49.3 B |
| CAGR (2025-2034) | 6.8% |
| Historical data | 2018-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | Rating/Power Output (Small Power Transformers, Medium Power Transformers, Large Power Transformers), Cooling Type (Oil-Cooled Transformers, Air-Cooled (Dry-Type) Transformers), Phase (Single-Phase Transformers, Three-Phase Transformers), Application (Power Generation Plants, Transmission and Distribution Utilities, Industrial Sector, Renewable Energy Integration) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Siemens Energy AG, Hitachi Energy Ltd., General Electric Company, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Schneider Electric SE, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation, Hyundai Electric & Energy Systems Co., Ltd., Eaton Corporation plc, Fuji Electric Co., Ltd., CG Power and Industrial Solutions Ltd., Hyosung Heavy Industries, EFACEC Power Solutions, MGM Transformer Company |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date