Wireless Telecom Infrastructure Market Size, Growth | CAGR 11.0%
Global Wireless Telecom Infrastructure Market Size, Share & Network Analysis By Infrastructure Type (Towers, Small Cells, DAS, Base Stations), By Technology (4G, 5G, Open RAN), By End User (Telecom Operators, Enterprises, Governments), Network Densification Trends, AI-Driven Optimization, Regional Outlook, Key Players & Forecast 2025–2034
Report Overview
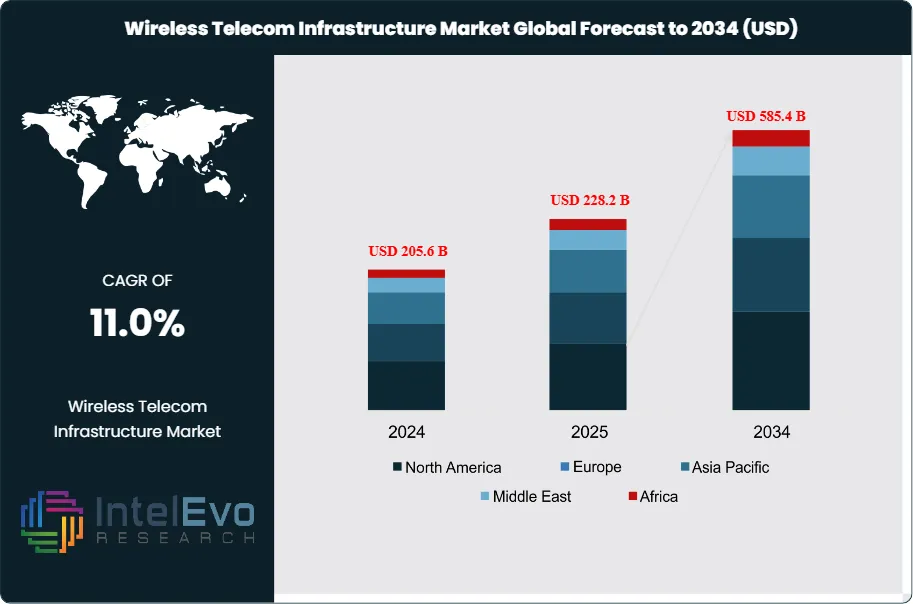
The Wireless Telecom Infrastructure Market is estimated at USD 205.6 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach approximately USD 585.4 billion by 2034, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 11.0% during 2025–2034. This sustained expansion is driven by accelerated 5G rollouts, rising mobile data traffic, and continuous investments in network densification through small cells and fiber backhaul. Governments and telecom operators are also prioritizing rural connectivity, private 5G networks, and infrastructure upgrades to support IoT, smart cities, and Industry 4.0 applications. As a result, wireless infrastructure remains a core enabler of digital economies and next-generation communication ecosystems worldwide.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportThis growth reflects the sector’s central role in enabling mobile connectivity, broadband expansion, and the transition to advanced network technologies. The market has expanded steadily over the past decade, supported by rising mobile penetration, surging data consumption, and the shift from 3G and 4G to 5G. In 2023, Asia-Pacific accounted for more than 35% of global revenue, valued at USD 67.1 billion, underscoring its position as the largest regional market.
Demand-side drivers remain strong. The proliferation of smartphones, streaming platforms, and connected devices continues to push network operators to expand coverage and capacity. The Internet of Things adds further pressure, with billions of devices requiring low-latency, high-speed connections. On the supply side, operators face the challenge of balancing capital expenditure with profitability, particularly as spectrum costs and infrastructure investments rise. Regulatory frameworks also influence deployment timelines, with spectrum allocation and site approvals varying widely across markets.
Technology is reshaping the sector. The rollout of 5G is accelerating adoption of small cell networks, distributed antenna systems, and advanced backhaul solutions. Artificial intelligence is increasingly applied to network optimization, predictive maintenance, and traffic management, improving efficiency in dense urban environments. By the end of 2022, the U.S. industry had deployed more than 142,000 cellular towers, 209,500 macrocell sites, and over 1.1 million indoor and outdoor small cell nodes, reflecting the scale of infrastructure required to sustain demand.
Investment activity highlights the strategic importance of infrastructure ownership. American Tower Corporation, with a market capitalization of USD 102.2 billion in early 2024, remains the global leader, while Crown Castle International and SBA Communications continue to expand their portfolios despite share price volatility. Data center operators such as Equinix and Digital Realty are also strengthening their role in supporting wireless networks through interconnection and colocation services.
Regional opportunities are shifting. While Asia-Pacific leads in scale, North America remains a critical investment hub due to high capital spending by operators such as Verizon, which allocated USD 10.5 billion in 2022 to network upgrades. Emerging markets in Africa and Latin America present long-term growth potential, particularly in rural connectivity where infrastructure gaps remain significant. For investors, the sector offers sustained growth prospects, anchored by rising data demand and the global transition to 5G and beyond.

Key Takeaways
- Market Growth: The global wireless telecom infrastructure market was valued at USD 205.6 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 585.4 billion by 2034, expanding at a CAGR of 11.0%. Growth is driven by rising mobile data consumption, 5G rollouts, and the surge in connected devices.
- Infrastructure Type: Base stations accounted for over 40% of total revenue in 2023. Their role in enabling wide-area coverage and supporting 5G deployment makes them the backbone of network expansion.
- Technology: The 4G/LTE segment held more than 64% share in 2023, reflecting its maturity and broad adoption. While 5G is expanding, 4G remains the primary technology supporting global mobile traffic.
- End Use: Telecom operators captured over 65% of market share in 2023. Their large subscriber bases and sustained capital expenditure on network upgrades continue to drive infrastructure demand.
- Driver: Rising demand for high-speed connectivity is a key growth factor. Global mobile data traffic is expected to grow at over 25% annually through 2030, requiring significant investment in towers, small cells, and backhaul systems.
- Restraint: High capital intensity and regulatory hurdles limit faster deployment. In the U.S., spectrum auctions and site approval delays add billions in costs and extend rollout timelines.
- Opportunity: Rural connectivity represents a major untapped market. Expanding infrastructure in underserved regions could unlock billions in new revenue, particularly in Africa and South Asia where mobile penetration is below 60%.
- Trend: Small cell deployment and AI-driven network optimization are reshaping infrastructure strategies. By 2022, the U.S. had installed over 1.1 million indoor and outdoor small cell nodes, highlighting the shift toward densification.
- Regional Analysis: Asia-Pacific led with over 35% share in 2023, supported by rapid 5G adoption in China, Japan, and South Korea. North America remains a high-investment region, with U.S. operators such as Verizon allocating more than USD 10 billion annually to network upgrades. Emerging markets in Latin America and Africa are expected to post double-digit CAGRs through 2033.
Infrastructure Type Analysis
By 2025, base stations continue to represent the largest share of the wireless telecom infrastructure market, accounting for more than 40% of total revenue. Their dominance reflects their role as the central interface between mobile devices and network infrastructure, enabling seamless transmission and reception of wireless signals. The exponential rise in mobile subscriptions, coupled with surging demand for high-speed data, has reinforced the need for dense and efficient base station networks.
The rollout of 5G has further accelerated investment in base stations. Unlike earlier generations, 5G requires a denser grid of small and macro base stations to deliver ultra-low latency and high-capacity connectivity. Operators in markets such as China, the United States, and South Korea have already deployed hundreds of thousands of 5G-ready base stations, with China alone surpassing 3 million installations by 2024. This scale of deployment underscores the infrastructure intensity required to sustain next-generation connectivity.
Emerging applications such as IoT, smart cities, and autonomous mobility are also reshaping infrastructure demand. These use cases require uninterrupted coverage and high reliability, driving operators to expand both macro and small cell deployments. The surge in video streaming and cloud-based services has added further pressure, making high-capacity base stations critical to maintaining quality of service.
Technology Analysis
As of 2025, 4G/LTE remains the most widely deployed wireless technology, accounting for more than 60% of global infrastructure revenue. Its dominance is supported by extensive coverage across urban and rural markets, as well as the large installed base of LTE-enabled devices. Despite the rapid expansion of 5G, LTE continues to serve as the backbone of mobile connectivity, particularly in emerging economies where 5G adoption is still in early stages.
The maturity of LTE networks has ensured consistent performance and affordability, making it the preferred choice for billions of users worldwide. Most smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices remain LTE-compatible, ensuring sustained demand for supporting infrastructure. Operators continue to invest in LTE upgrades, particularly in spectrum refarming and advanced LTE features, to extend the lifecycle of their networks.
At the same time, 5G is gaining momentum, with global connections expected to surpass 2 billion by 2025. The transition, however, is gradual due to high capital requirements and spectrum availability constraints. As a result, operators are pursuing hybrid strategies, maintaining LTE as a foundational layer while expanding 5G coverage in high-demand urban corridors. This dual-track approach ensures continuity of service while preparing networks for future applications such as industrial automation and immersive media.
End-Use Analysis
Telecom operators remain the dominant end-users of wireless telecom infrastructure, accounting for more than 65% of global market share in 2025. Their leadership stems from their role as primary service providers, managing vast subscriber bases and investing heavily in network expansion. In 2024 alone, U.S. operators allocated over USD 12 billion to infrastructure upgrades, while Chinese carriers collectively invested more than USD 20 billion in 5G rollouts.
The scale of investment reflects the pressure operators face to meet rising data consumption, which continues to grow at double-digit rates annually. With mobile video accounting for more than 70% of global data traffic, operators are compelled to expand capacity through new towers, base stations, and backhaul systems. Their partnerships with infrastructure providers and equipment vendors further strengthen their ability to deploy advanced solutions at scale.
Enterprises and government agencies are emerging as secondary demand drivers. Enterprises are increasingly investing in private 5G networks to support industrial automation, logistics, and secure communications. Governments, meanwhile, are prioritizing infrastructure development to support digital transformation agendas, particularly in smart city projects and public safety networks. While smaller in share, these segments represent high-growth opportunities through 2030.
Regional Analysis
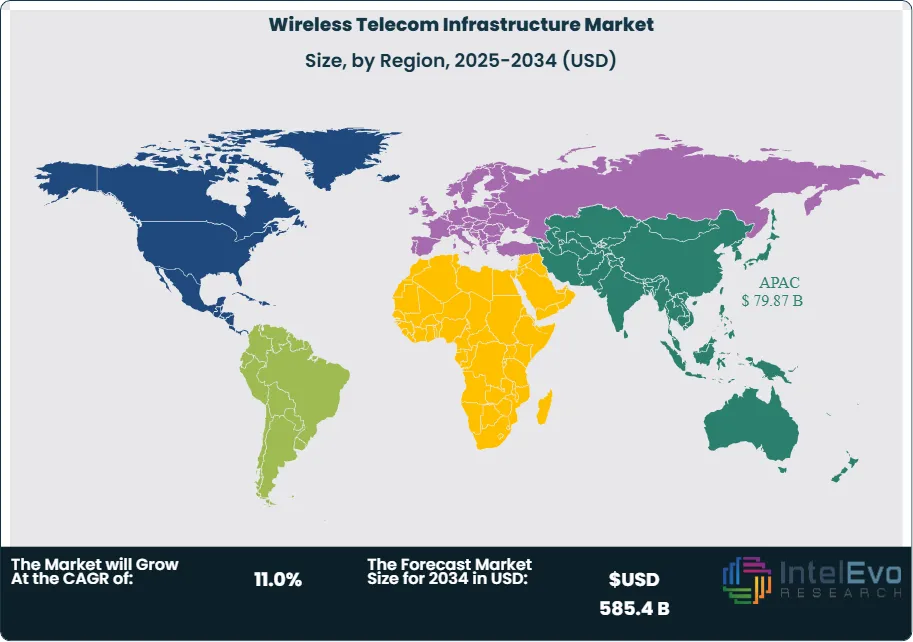
Asia Pacific continues to lead the global market in 2025, accounting for more than 35% of total revenue. The region’s dominance is anchored by large-scale 5G deployments in China, South Korea, and Japan, supported by strong government backing and aggressive operator investments. China alone has committed to expanding 5G coverage to all prefecture-level cities by 2025, creating significant demand for base stations, antennas, and backhaul systems.
North America remains a critical investment hub, driven by high consumer data usage and rapid adoption of advanced wireless services. U.S. operators such as Verizon and AT&T have allocated multi-billion-dollar budgets annually to expand 5G coverage, with a strong focus on small cell deployments in urban centers. The region also benefits from a robust ecosystem of infrastructure providers, including American Tower and Crown Castle, which continue to expand their portfolios.
Europe is progressing steadily, with operators balancing 5G rollouts against regulatory and cost challenges. Countries such as Germany, the UK, and France are leading adoption, while Eastern Europe presents long-term growth potential. Meanwhile, Latin America and the Middle East & Africa are emerging as high-growth regions, with double-digit CAGRs projected through 2030. Infrastructure expansion in these markets is driven by rising mobile penetration, government-led digital initiatives, and the need to bridge rural connectivity gaps.
Get More Information about this report -
Request Free Sample ReportKey Market Segments
Infrastructure Type
- Base Stations
- Antennas
- Transceivers
- Backhaul Equipment
- Other Infrastructure Types
Technology
- 4G/LTE
- 5G
- Other Technologies
End-User
- Telecom Operators
- Enterprises
- Government and Public Sector
- Other End-Users
Regions
- North America
- Latin America
- East Asia And Pacific
- Sea And South Asia
- Eastern Europe
- Western Europe
- Middle East & Africa
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market size (2024) | USD 205.6 B |
| Forecast Revenue (2034) | USD 585.4 B |
| CAGR (2024-2034) | 11.0% |
| Historical data | 2018-2023 |
| Base Year For Estimation | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025-2034 |
| Report coverage | Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Market Dynamics, Growth Factors, Trends and Recent Developments |
| Segments covered | Infrastructure Type (Base Stations, Antennas, Transceivers, Backhaul Equipment, Other Infrastructure Types), Technology (4G/LTE, 5G, Other Technologies), End-User (Telecom Operators, Enterprises, Government and Public Sector, Other End-Users) |
| Research Methodology |
|
| Regional scope |
|
| Competitive Landscape | Ericsson, Vertical Bridge, Samsung, Crown Castle, American Tower Corporation, ZTE, SBA Communications, TowerCo, AT&T Towers, Nokia, Mobilitie, Other Key Players |
| Customization Scope | Customization for segments, region/country-level will be provided. Moreover, additional customization can be done based on the requirements. |
| Pricing and Purchase Options | Avail customized purchase options to meet your exact research needs. We have three licenses to opt for: Single User License, Multi-User License (Up to 5 Users), Corporate Use License (Unlimited User and Printable PDF). |
Select Licence Type
Connect with our sales team
Wireless Telecom Infrastructure Market
Published Date : 03 Jan 2026 | Formats :Why IntelEvoResearch
100%
Customer
Satisfaction
24x7+
Availability - we are always
there when you need us
200+
Fortune 50 Companies trust
IntelEvoResearch
80%
of our reports are exclusive
and first in the industry
100%
more data
and analysis
1000+
reports published
till date